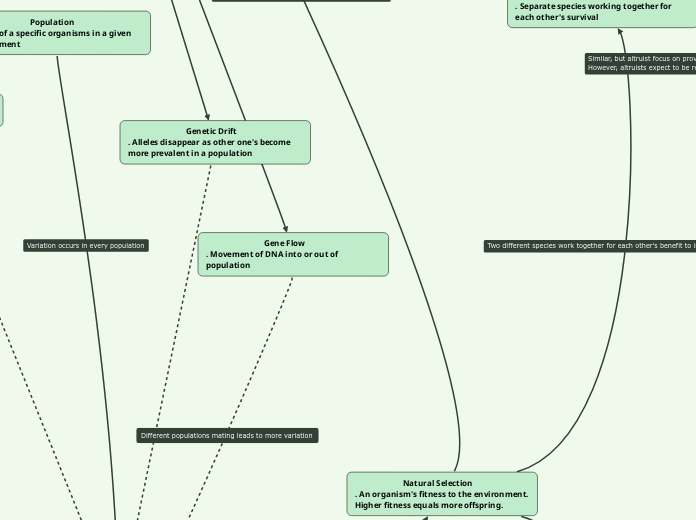
Population
. Group of a specific organisms in a given environment
Variation
. Different alleles and traits in a population that can reduce or increase fitness
Natural Selection
. An organism's fitness to the environment. Higher fitness equals more offspring.
Sex
. The trading of DNA between males and females
Random Mutation
. A mutation on an allele that can be beneficial or detrimental to the organism. Random chance.
Genetic Recombination
. The crossing over of DNA during meiosis produces change and variation in the offspring's DNA. Mutations can occur during this time
Transposons
. Jumping alleles that can copy themselves multiple times on a DNA chain
Particulate Inheritance
. Unseen alleles that still exist in a population that can see resurgence in a population
Gene Flow
. Movement of DNA into or out of population
Horizontal Gene Transfer
. Bacteria share DNA through the environment and is directly taken and placed onto DNA
Mutualism
. Separate species working together for each other's survival
Altruism
. When an individual performs an action that is costly to itself in order to benefit another. But does the cost out way the benefit determines this behavior.
Reproductive Isolation
. Species inability to breed successfully
Speciation
. Distinct species in the course of evolution
Group Selection
. Groups of organisms are affected by natural selection instead of individuals.
Kin Selection
. Organisms are more likely to behave altruistically to kin or siblings that share DNA.