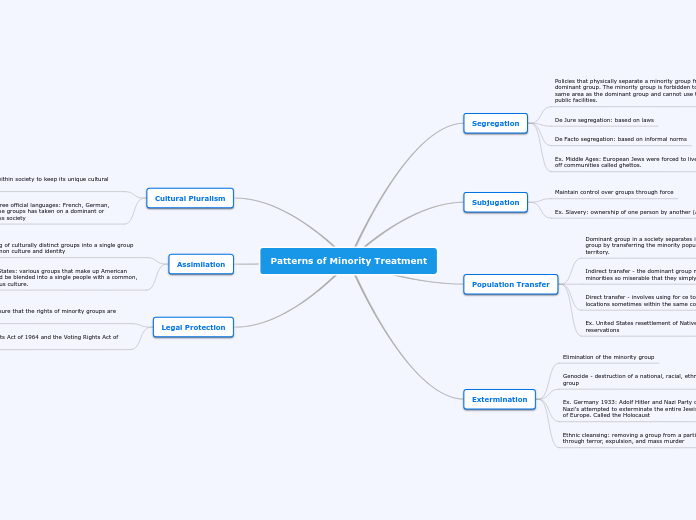
Patterns of Minority Treatment
Segregation
Policies that physically separate a minority group from the dominant group. The minority group is forbidden to live in the same area as the dominant group and cannot use the same public facilities.
De Jure segregation: based on laws
De Facto segregation: based on informal norms
Ex. Middle Ages: European Jews were forced to live in walled off communities called ghettos.
Subjugation
Maintain control over groups through force
Ex. Slavery: ownership of one person by another (Apartheid)
Population Transfer
Dominant group in a society separates itself from a minority group by transferring the minority population to a new territory.
Indirect transfer - the dominant group makes life for minorities so miserable that they simply leave
Direct transfer - involves using for ce to move people to new locations sometimes within the same country
Ex. United States resettlement of Native Americans on reservations
Extermination
Elimination of the minority group
Genocide - destruction of a national, racial, ethnic, or religious group
Ex. Germany 1933: Adolf Hitler and Nazi Party come to power. Nazi's attempted to exterminate the entire Jewish population of Europe. Called the Holocaust
Ethnic cleansing: removing a group from a particular area through terror, expulsion, and mass murder
Cultural Pluralism
allows each group within society to keep its unique cultural identity.
Ex. Switzerland - three official languages: French, German, Italian (none of these groups has taken on a dominant or minority role in Swiss society
Assimilation
The blending of culturally distinct groups into a single group with a common culture and identity
Ex. United States: various groups that make up American society could be blended into a single people with a common, homogeneous culture.
Legal Protection
Legal steps to ensure that the rights of minority groups are protected.
Ex. The Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965