Print Ads
Physiological / Persuasive Techniques
Presuasive Techniques
Strategies used to influence an audience to adopt a specific idea or take action, primarily through Aristotle's ethos (ethics/credibility), pathos (emotion), and logos (logic).
Endorsements
The act of publicly supporting or recommending something, whether it's a product, person or idea. Consequently, establishing credibility is a crucial component in shaping consumer perceptions and driving sales.

Logos
A logical approach involves relying on the intelligence of the audience in support of your advertisement and providing evidence to support your claims.
Pathos
To persuade by appealing to the audience’s emotions, you want the audience to feel the same emotions you feel about your product, you want to emotionally connect with them and influence them.

Propaganda Techniques
Methods used to manipulate public opinion, often by exploiting emotions, distorting facts, or simplifying complex issues to persuade an audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take a specific action.

Bandwagon
The bandwagon effect capitalizes on the idea that people like to follow the crowd. By suggesting that “everyone is doing it” in your visual advert, you can persuade individuals to join in the same experience to avoid feeling left out.
Linguistics / Textual Techniques
Hyperbole Refers to exaggeration and used to emphasize a point which works great as an advertising technique

An example of a hyperbole used in print ads is through the original Mars bars slogan "A Mars a day helps you work, rest and play."
Rhetorical Questions These questions are asked to engage the audience rather than to receive a response
An example of rhetorical question used in print ads in where a children's clothing store is being promoted with the headline being "Kids grow up quickly, don't they" which is asked regardless of having an obvious answer.
Alliteration
It uses repeating rhythms/sounds and it is used in print ads because the repetition of sounds makes the ad memorable and catchy.

Message (Krishna)
Target Audience / Placement
What is it?
The target audience is the final viewer of the advertisement, someone with an intent to purchase or interact with the product. The effectiveness of a print ad depends on reaching its target audience
Print-ads can be placed in Traditional Media Placements (Billboards, Newspapers, Radio) or in Digital Advertising (Website Banners)
How does it work?
Effectively reaching the target audience depends on emotional appeal, story telling and placementThe message of a print-ad reaches its intended demographics better when placed in proximity
Ex: the placement of running shoe ads next to water bottle booths in marathons

HOKA 2025 Chicago Marathon
Instilling Urgency

Nike 2025 London Marathon
How does it work?
Choosing to word the message in a way to increase urgency can provoke and idea of scarcity, enticing the customer to purchase the product
Ex: A sale that ends soon can create a sense of FOMO that causes people to buy the products faster
What is it?
Instilling urgency follows the principle of creating a parth of least resistance; reducing the friction between a customer purchasing a product
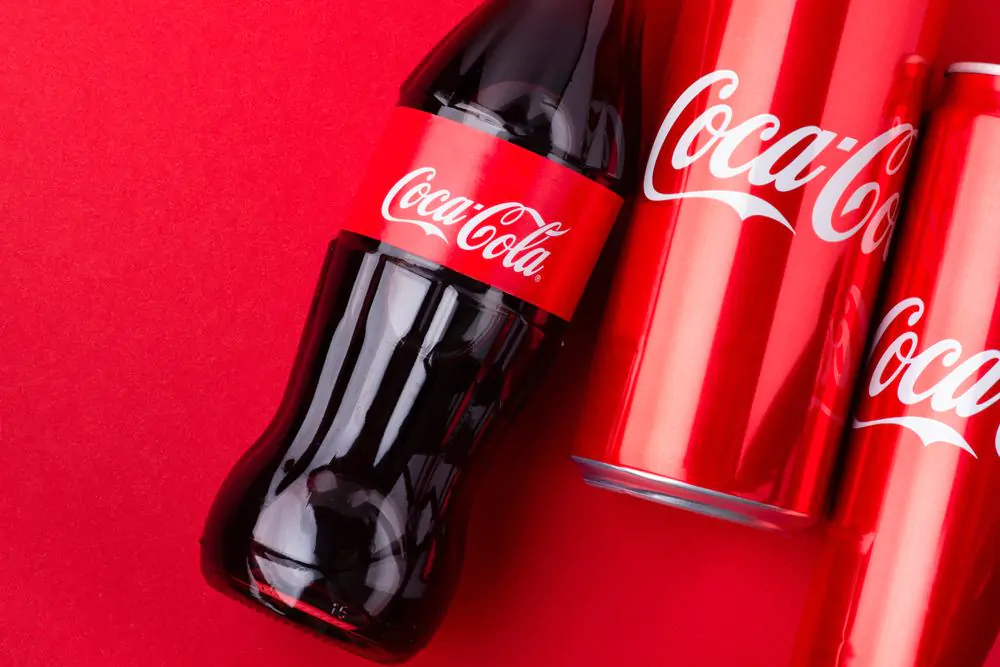
Emotional Appeal

Coca-Cola 2009 #open-happiness
How does it work?
According to neuromarketing, emotion based advertising is more effective than logical advertising, meaning stylistic choices to provoke emotions can be more influential in purchase decisions
What is it?
Emotional Appeal in advertising refers to the usage of visuals, texts and sometimes sounds to provoke an emotional response in the viewer
Story Telling & Narration
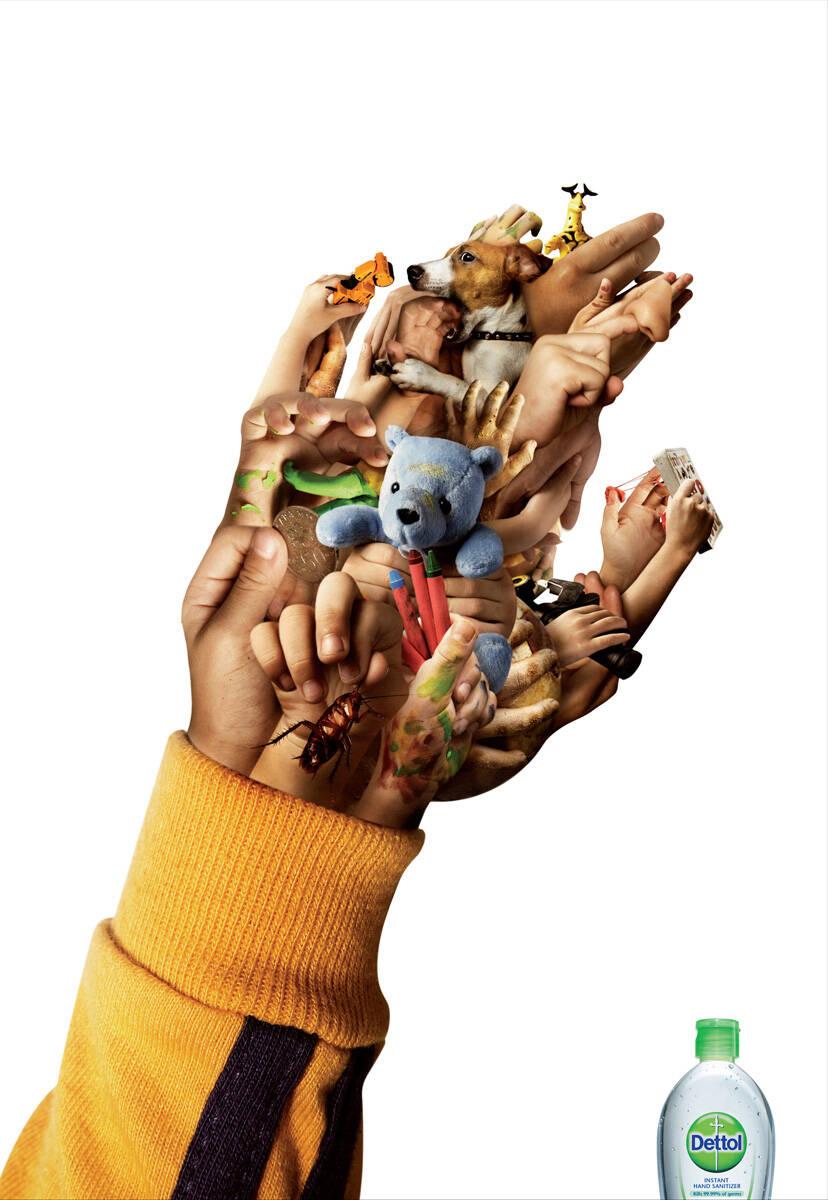

Detol Malaysia 2008 Child's Hand
How does it work?
Studies reveal that print ads in magazines are 1.7 times more likely to be recalled and talked about than other ads, with talkability and story telling being the main influential factors
What is it?
Story telling / Narration refers to the ability for an advertisement to display a story subliminally from its main front image
Visual / Design Techniques
Typography:
Typography sets the tone of the ad by choosing fonts that reflect the brand’s personality and message. It guides the reader’s eye and ensures key information stands out.
Imagery
Strong imagery grabs attention and creates an emotional connection with the audience. In print ads, visuals often communicate the message faster than words.
Colour Theory/Psychology
Colors influence emotions and perceptions, shaping how the audience feels about the ad. The right color palette can highlight important elements and reinforce brand identity.
Elements of design
Balance, contrast, alignment, and hierarchy help organize information effectively. These elements make the ad visually appealing and easy to read.