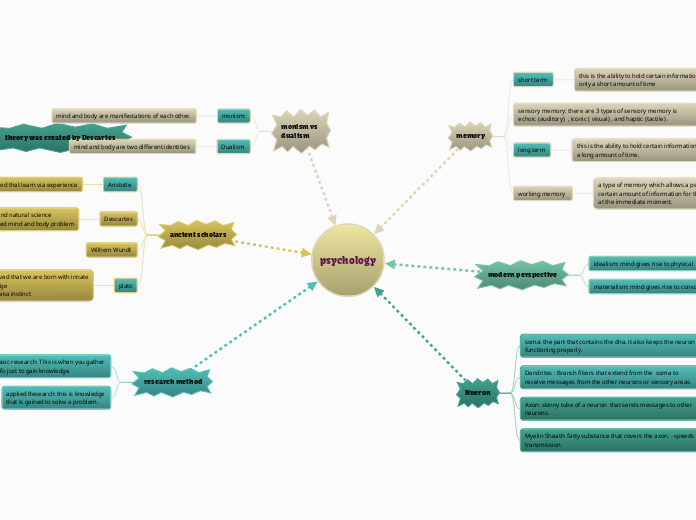
psychology
memory
short term
this is the ability to hold certain information or memory for
only a short amount of time
sensory memory: there are 3 types of sensory memory is echoic (auditory) , iconic ( visual) , and haptic (tactile) .
long term
this is the ability to hold certain information or memory for
a long amount of time.
working memory
a type of memory which allows a person to temporarily hold a certain amount of information for the sole puprose of using it at the immediate moment.
modern perspective
idealism: mind gives rise to physical
materialism: mind gives rise to consciousness
Nueron
soma: the part that contains the dna. it also keeps the neuron functioning properly.
Dendrites : Branch fibers that extend from the soma to receive messages from the other neurons or sensory areas.
Axon: skinny tube of a neuron that sends messages to other neurons.
Myelin Sheath: fatty substance that covers the axon. - speeds transmission.
monism vs dualism
monism:
mind and body are manifestations of each other.
Dualism
mind and body are two different identities
ancient scholars
Aristotle
believed that learn via experience
Descartes
-Reason and natural science
- introduced mind and body problem
Wilhem Wundt
plato
he believed that we are born with innate
knowledge
-nature aka instinct
research method
basic research: This is when you gather
info just to gain knowledge.
applied Research: this is knowledge
that is gained to solve a problem.