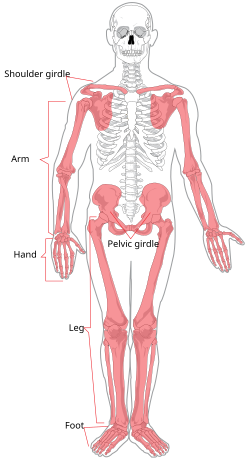
SKELETAL SYSTEM
upper and lower extermities, shoulder and hip bones
skull,ribs and vertebrae

Ligaments
Connect muscle to bone

Joints
Hinge joint
elbow
knee
Pivot joint
neck
Imovable joint
skull
gliding joint
wrist
ankle
Ball socket joint
hips
shoulders

Tendon
Connects muscle to bone

5 major functions
stores minerals
to make blood cells
for structure
movement
protect organs
Spongy Bone
Light wieght, strong, many spaces
Boens are hard
They are made up of hard minerals-calcium and phosporus
Compact Bone
very hard, not solid
many small canals, where blood vesels enter and leave
Outer membrane
where blood vessels and nerves enter and leave bone

Marrow
Red Marrow
Red blood cells made
Yellow Marrow
Fat is stored
MUSCULAR SYSTEM
Injuries
Cramp
muscel contracts strongly
Tear
Muscel streches to far, pulled apart
Happens when muscels are over-worked
How Muscels Work
one contracts, one relaxes
Muscels release energy from breaking down gluose
Muscel Control
Voluntary
You dont have to think about it
Ex. Running, turning a book
Involuntary
Muscel you control
Ex. Cardiac
Types Of Muscel
Skeletal
attached to skeleton
React and tire quickly
attached to bone by tendon
Smooth
Found In internal organs
React slow, does'nt tire easy
Cardiac
found in heart
does'nt tire quickly