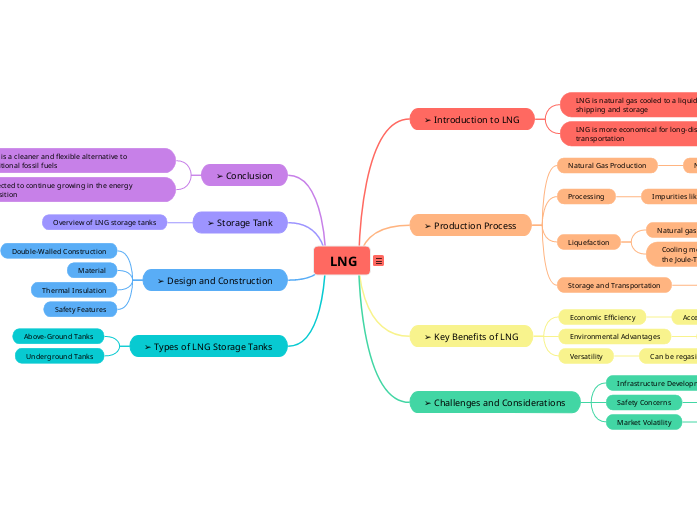
LNG
➢ Introduction to LNG
LNG is natural gas cooled to a liquid state for shipping and storage
LNG is more economical for long-distance transportation
➢ Production Process
Natural Gas Production
Natural gas is extracted through drilling
Processing
Impurities like water
carbon dioxide
and sulfur compounds are removed
Liquefaction
Natural gas is cooled to convert it into a liquid state
Cooling methods include refrigeration cycles and the Joule-Thomson effect
Storage and Transportation
LNG is stored in cryogenic tanks and transported via LNG carriers
➢ Key Benefits of LNG
Economic Efficiency
Access to remote or stranded gas fields
Environmental Advantages
Fewer emissions compared to coal or oil
Versatility
Can be regasified and used for various applications
➢ Challenges and Considerations
Infrastructure Development
Significant investment and planning required
Safety Concerns
Specialized equipment and safety protocols needed
Market Volatility
Prices influenced by supply and demand dynamics
➢ Conclusion
LNG is a cleaner and flexible alternative to traditional fossil fuels
Expected to continue growing in the energy transition
➢ Storage Tank
Overview of LNG storage tanks
➢ Design and Construction
Double-Walled Construction
Material
Thermal Insulation
Safety Features
➢ Types of LNG Storage Tanks
Above-Ground Tanks
Underground Tanks