THE GENERATIONS OF COMPUTERS
Each one of the five generations of computers is characterized by a major technological development that fundamentally changed the way computers operate.
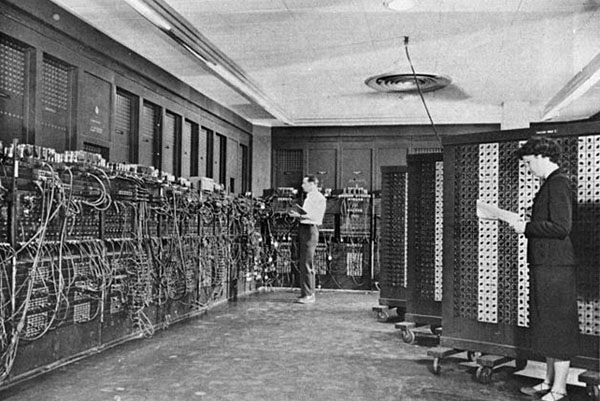
First Generation: Vacuum Tubes (1940-1956)
• Its main component was vacuum tubes as circuits and magnetic drums as memory.
• These computers were very expensive to operate and in addition to using a great deal of electricity, the first computers generated a lot of heat, were often enormous, and It would take operators days or even weeks to set-up a new problem.
• Input was based on punched cards and paper tape, and output was displayed on printouts.

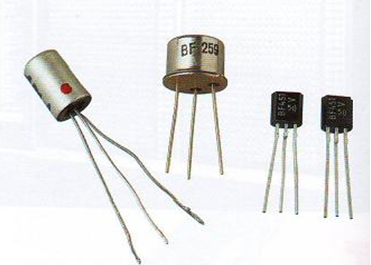
Second Generation: Transistors (1956-1963)
• Its main component was transistors that allow computers to become smaller, faster, cheaper, more energy-efficient and more reliable
• The transistor still generated a great deal of heat that subjected the computer to damage, it was a vast improvement over the vacuum tube.
• Second-generation computers still relied on punched cards for input and printouts for output.
• The first computers of this generation were developed for the atomic energy industry.
Third Generation: Integrated Circuits (1964-1971)
• Its main component was silicon chips, called semiconductors as integrated circuits, which dramatically increased the speed and efficiency of computers.
• The punched cards and printers were replaced by user interaction with keyboards and monitors and an operating system that functions as a bridge of exchange.
• The computer was already multitasking and multifunctional thanks to the large number of applications they created and a large central program that controlled memory.
• Computers for the first time became accessible to a mass audience because they were smaller and cheaper than their predecessors.
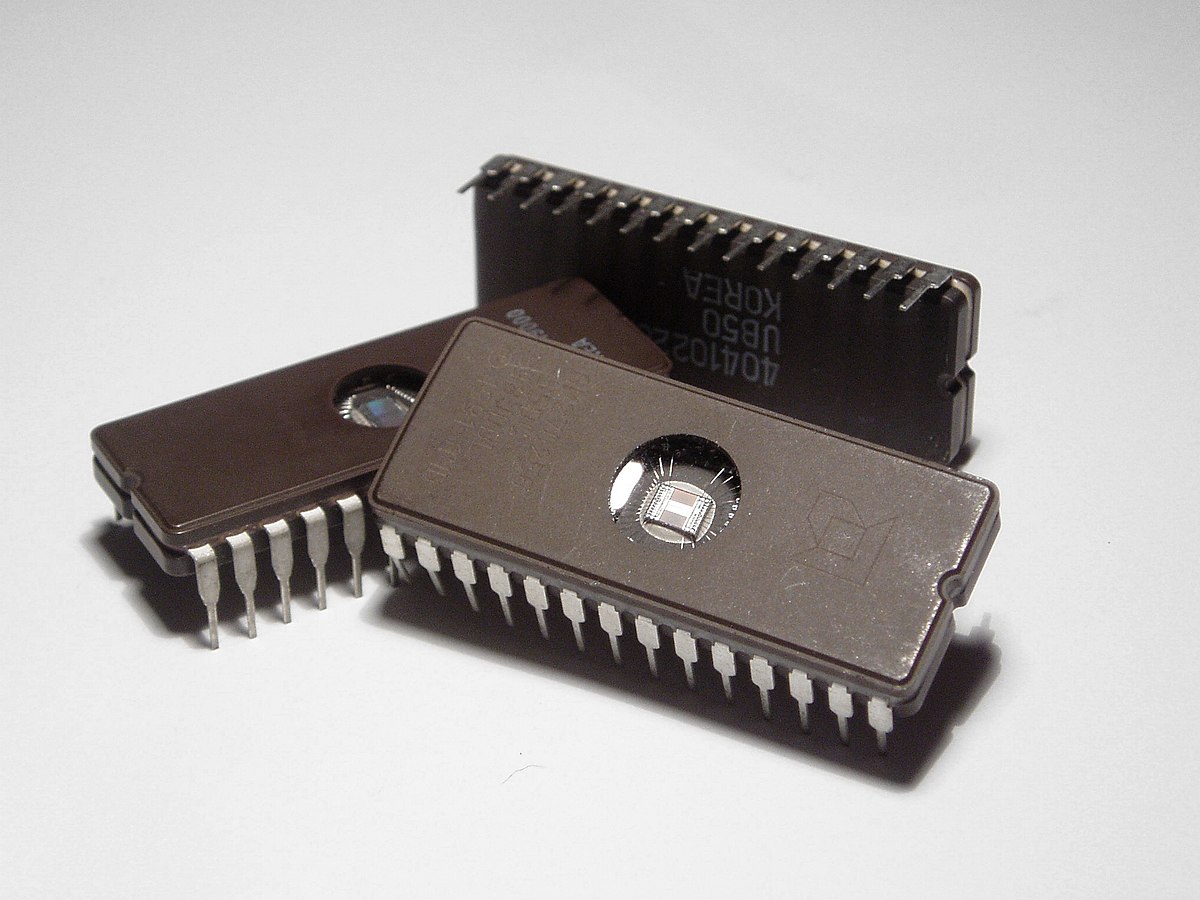
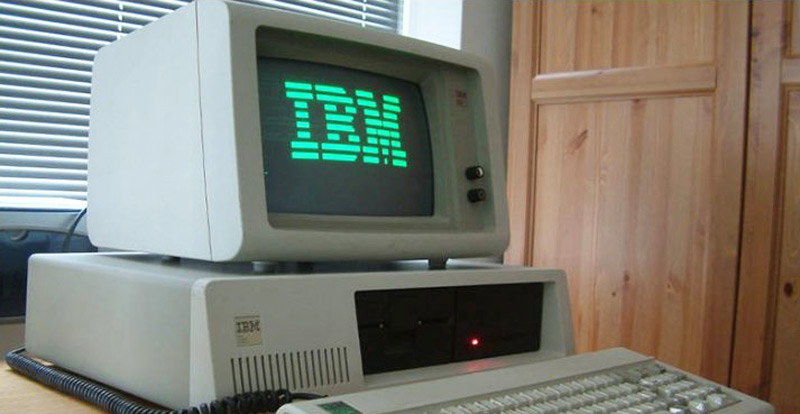
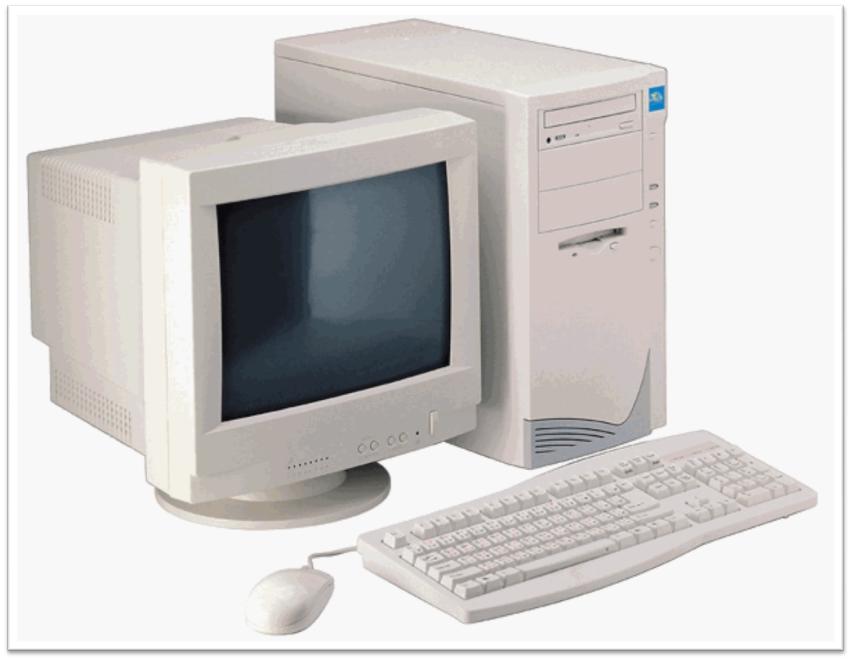
Fourth Generation: Microprocessors (1971-Present)
• Its main component was the microprocessor that already brought thousands of integrated circuits built on a single silicon chip. I put all the components of the computer, from the central processing unit and memory to the input / output controls, on a single chip.
• In 1981 IBM introduced its first computer for the home user, and in 1984 Apple introduced the Macintosh.
• Microprocessors also moved out of the realm of desktop computers and into many areas of life as more and more everyday products began to use microprocessors.
• Fourth generation computers also saw the development of GUIs, the mouse and handheld devices.
Fifth Generation: Artificial Intelligence (Present and Beyond)
• Its main component is based on artificial intelligence, are still in development, though there are some applications, such as voice recognition, that are being used today.
• The use of parallel processing and superconductors is helping to make artificial intelligence a reality.
• The goal of fifth-generation computing is to develop devices that respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and self-organization.