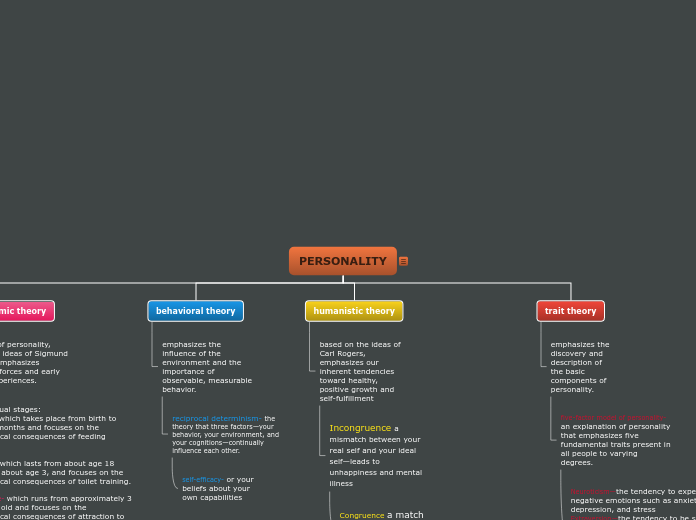
a person’s distinctive and stable way of thinking, feeling, and behaving.
explanation of personality, based on the ideas of Sigmund Freud, that emphasizes unconscious forces and early childhood experiences.
psychosexual stages: oral stage- which takes place from birth to about 18 months and focuses on the psychological consequences of feeding behavior.
anal stage- which lasts from about age 18 months to about age 3, and focuses on the psychological consequences of toilet training.
phallic stage- which runs from approximately 3 to 6 years old and focuses on the psychological consequences of attraction to the opposite-sex parent.
latency stage- which lasts through the elementary school years, when puberty has not yet kick-started the child’s sexual drive, and the child’s energies are focused primarily on school
genital stage- which lasts from puberty through adulthood and focuses on mature, adult sexual relationships.
emphasizes the influence of the environment and the importance of observable, measurable behavior.
reciprocal determinism- the theory that three factors—your behavior, your environment, and your cognitions—continually influence each other.
self-efficacy- or your beliefs about your own capabilities
based on the ideas of Carl Rogers, emphasizes our inherent tendencies toward healthy, positive growth and self-fulfillment
Incongruence a mismatch between your real self and your ideal self—leads to unhappiness and mental illness
Congruence a match between your real self and your ideal self.
real self is the version of yourself that you actually experience in your day-to-day life, where you feel pressure to live up to the conditions of worth that others put on you. ideal self is the self-actualized version of yourself that you naturally strive to become
emphasizes the discovery and description of the basic components of personality.
five-factor model of personality- an explanation of personality that emphasizes five fundamental traits present in all people to varying degrees.
Neuroticism—the tendency to experience negative emotions such as anxiety, depression, and stress
Extraversion—the tendency to be socially outgoing
Openness to experience—the tendency to be receptive to new or unconventional ideas
Conscientiousness—the tendency to be organized, responsible, and deliberate
Agreeableness—the tendency to cooperate and comply with other people
OCEAN