Patterns in minority group treatment
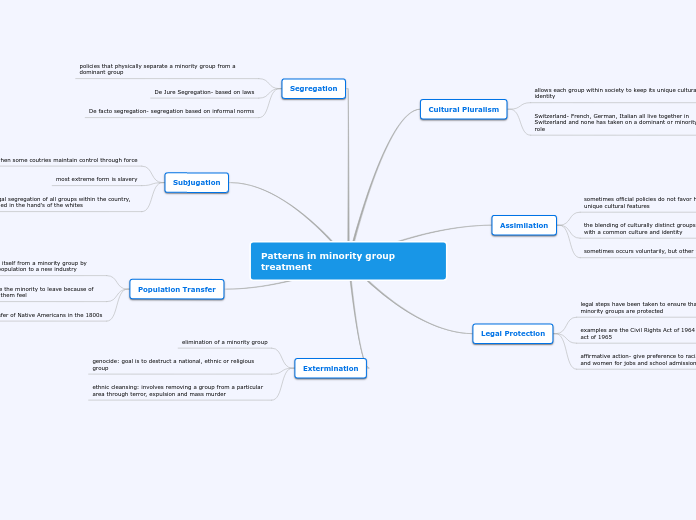
Cultural Pluralism
allows each group within society to keep its unique cultural identity
Switzerland- French, German, Italian all live together in Switzerland and none has taken on a dominant or minority role
Assimilation
sometimes official policies do not favor holding on to their unique cultural features
the blending of culturally distinct groups into a single group with a common culture and identity
sometimes occurs voluntarily, but other times it is forced
Legal Protection
legal steps have been taken to ensure that the rights f minority groups are protected
examples are the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting rights act of 1965
affirmative action- give preference to racial dn ethic minorities and women for jobs and school admission
Segregation
policies that physically separate a minority group from a dominant group
De Jure Segregation- based on laws
De facto segregation- segregation based on informal norms
Subjugation
when some coutries maintain control through force
most extreme form is slavery
apartheid- legal segregation of all groups within the country, power remained in the hand's of the whites
Population Transfer
dominant group separates itself from a minority group by transferring the minority population to a new industry
the dominant people cause the minority to leave because of how miserable they make them feel
examples:direct transfer of Native Americans in the 1800s
Extermination
elimination of a minority group
genocide: goal is to destruct a national, ethnic or religious group
ethnic cleansing: involves removing a group from a particular area through terror, expulsion and mass murder