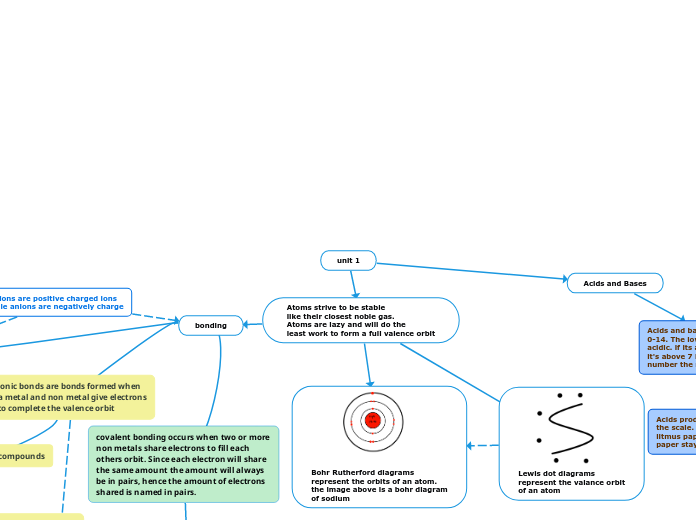
unit 1
Atoms strive to be stable
like their closest noble gas.
Atoms are lazy and will do the
least work to form a full valence orbit
bonding
ionic bonds are bonds formed when
a metal and non metal give electrons
to complete the valence orbit
naming ionic compounds
Use the name of the first element,
then add the stem of the second element
and add the ending "ide".
covalent bonding occurs when two or more
non metals share electrons to fill each others orbit. Since each electron will share the same amount the amount will always be in pairs, hence the amount of electrons shared is named in pairs.
Polyatomic ions
are a group of atoms that carry an
and overall charge
When naming covalent compounds
add the first element, then the second
element adding the ending ide. Then add a prefix at the beginning of the second element stating the amount of that element
Covalent bonds don't have
fixed ratios, so we use the latin
prefixes for them.
Bohr Rutherford diagrams
represent the orbits of an atom.
the image above is a bohr diagram
of sodium
Lewis dot diagrams
represent the valance orbit
of an atom
Cations are positive charged ions
while anions are negatively charge
Writing formulas
When Writing formulas you write the
metal first then the non metal, also in subscript next to the element write the amount of that element.
multivalent elements can
carry multiple charges, a list of
potential charges are listed on the top
left of the element on the periodic table.
when writing out the the compound element you use the roman numerals to list the charge. Do NOT use roman numerals when writing out the formula.
Acids and Bases
Acids produce H+ ions and are below 7 on the scale. react with some metals. Blue litmus paper turns red in acids, red litmus paper stays.
There are two types of acids:
oxyacids and binary acids
When naming binary acids
use hydro as the prefix, then add
the stem name of the 2nd element,
add ic as the ending.