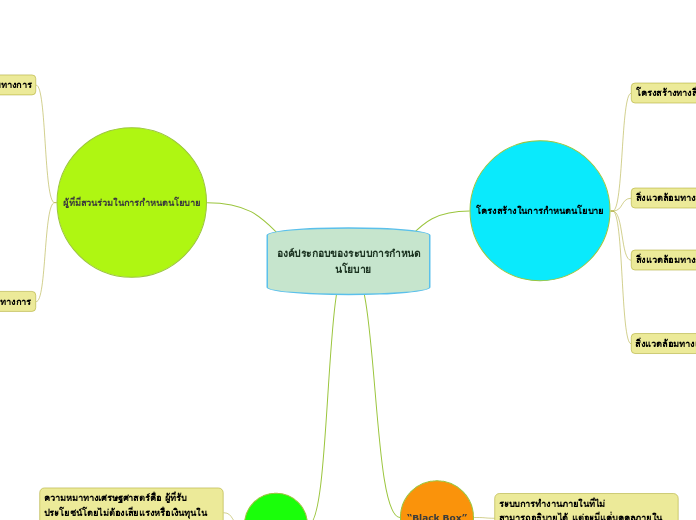
องค์ประกอบของระบบการกำหนด
นโยบาย
Tenses demonstrate the time of actions centered around the subject of the sentence. These actions are called verbs and change according to tenses.
Free rider
ความหมายทางสังคมคือ กาฝาก
ความหมาทางเศรษฐศาสตร์คือ ผู้ที่รับประโยชน์โดยไม่ต้องเสียแรงหรือเงินทุนในการผลิต
ผู้ที่มีสวนร่วมในการกำหนดนโยบาย
There are four Future tenses:
- Future Simple ('with Will' and 'with Going to')
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
แบบไม่ทางการ
Future Continuous is used:
- for an action that is likely to happen in the future and continue for an expected length of time
- for an action that will be in progress at some point in the future
- for action verbs (e.g. running)
- for predictions about future events
Adverb used with Future Continuous:
- tomorrow (e.g. tomorrow at 5 o'clock)
จะประกอบไปด้วยผู้มีบทบาทในกระบวนการนโยบายที่ไม่มีคำอธิบายโดยตรง ซึ่งคนกลุ่มนี้จะทำเพื่อประผดยชน์สวนตน
Structure:
Subject + Will Be + Verb-ING
e.g. You will be having fun at the party.
สื่อมวลชน
ให้ข้อมูลของผลเมืองเกี่ยวกับประเด็นต่างๆในสังคม
กลุ่มคณะที่ปรึกษาและองค์การวิจัยอื่นๆ
จัดการข้อมูลต่างๆเพื่อกำหนดนโยบาย
พรรคการเมือง
การออกนโยบายของแต่ละพรรคเพื่อให้ประชาชนเลือกหรือ
สนใจพรรคของตน
ปัจเจกชน
ผู้มีอำนาจ
ผู้มีอิทธิผล
กลุ่มผลประโยชน์
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I will be beingYou will be beingHe/She/It will be beingWe will be beingYou will be beingThey will be being
Form of verb 'to have':
I will be havingYou will be havingHe/She/It will be havingWe will be havingYou will be havingThey will be having
การรวมกลุ่มของผู้คนเพื่อเรียกร้องสิทธิของตน
เช่น การเรียกร้องของกลุ่ม LGBT
แบบทางการ
Future Simple is used:
- to predict an event in the future
- to invite
- to give orders
- to express willingness
- for actions that have not yet occurred but that will occur at a future date
มีภาระหน้าที่รับผิดชอบจะถูกแทรกแซงผ่านทางกฎหมาย และพวกเขาเหล่านั้นจะมีอำนาจ
ในการกำหนดให้เกิดเป็นนโยบายขึ้นมา
Future Simple with 'will'' is used:
- to predict the future
- for something with absolute certainty
- when we're talking about a decision at the moment of speaking
- promises, requests, refusals, offers
- future facts
Some adverbs used with Future Simple:
- tomorrow
- next week
- next month
- next year
สถาบันตุลาการ
Structure:
Will + Subject + V1(First Form of Verb)?
e.g. Will you see Mary when she comes back from Denmark?
สนับสนุนในการแบ่งแยกประเด็นทางการเมืองและทางกฎหมาย
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
Will I be?Will you be?Will he/she/it be?Will we be?Will you be?Will they be?
Form of word "to have":
Will I have?Will you have?Will he/she/it have?Will we have?Will you have?Will they have?
สถาบันการบริหาร
Structure:
Subject + Won’t (will not) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. You won’t see Mary when she comes back from Denmark.
ผู้บริหารมีอำนาจสูงสุดในการบริหารประเทศ สามารถใช้สิทธิได้อย่างเต็มที่ในการพิจารณา
ข้อดีในองค์การและเป็นเพียงคนเดียวที่จะนำพาให้ผู้ทำงานสามารถทำงาน
ให้บรรลุเป้าหมายของการบริหารขององค์การ
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
I will not beYou will not beHe/She/It will not beWe will not beYou will not beThey will not be
Form of word "to have":
I will not haveYou will not haveHe/She/It will not haveWe will not haveYou will not haveThey will not have
สภานิติบัญญัติ
Structure:
Subject + Will + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I will see Mary when she comes back from Denmark.
มีหน้าที่ออกกดหมายเพื่อที่จะสร้างนโยบาย แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม กลุ่มผลประโยชน์ก็ยังคงมุ่งมั่นที่
จะเปลี่ยนแปลงนโยบายให้ได้
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I will beYou will beHe/She/It will beWe will beYou will beThey will be
Form of verb 'to have':
I will haveYou will haveHe/She/it will haveWe will haveYou will haveThey will have
“Black Box”
There are four Past tenses:
- Past Simple
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect Simple
- Past Perfect Continuous
ระบบการทำงานภายในที่ไม่
สามารถอธิบายได้ แต่จะมีแค่่บุคคลภายในเท่านั้นที่สามารถรับรู้ได้
Past simple expresses:
- an action that happened in the past and has no connection with the present
- an action that happened once in the past
- an action that happened regularly in the past
- an action that was true for some time in the past
- an event or action that already occurred
- an action that is finite - has both a starting and a stopping point
Some adverbs used with Past Simple:
- yesterday
- last month, last year
- ago (e.g. two days ago)
- in (e.g. in 1997)
- never, always, seldom, often, frequently, occasionally, once, twice
โครงสร้างในการกำหนดนโยบาย
There are four Present tenses:
- Present Simple
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
สิ่งแวดล้อมทางเศรษฐกิจ
Present Perfect Continuous is used:
- to describe an action that started in the past and has continued up to the present
- to describe an action that has just finished
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect Continuous:
- always
- only
- never
- ever
- still
- just
สิ่งแวดล้อมทางเศรษฐกิจครอบคลุมไปด้วยการเจริญเติบโตทางเศรษฐกิจ ความมั่งคั่งทางสังคม ขนาดของอุตสาหกรรม ค่าเฉลี่ยของ
การเติบโตทางเศรษฐกิจ ภาวะเงินเฟ้อ ค่าจ้างแรงงาน เป็นต้น ที่กล่าวมาข้างต้นมีความสำคัญมากเพราะสามารถนำมากำหนดนโยบาย
Structure:
Subject + have/ has been + Verb-ING
e.g. They have been learning French for two years.
สิ่งแวดล้อมทางการเมือง
Present Perfect is used for:
- an action that occurred at a time which is indefinite and has its effect on the subject
- an action that occurred many times and has the possibility to occur in the present/future
- an action that began in the past and is still going on in the present
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect:
- just
- already
- yet
- for
- never/ever
- up to now
มีแนวทางหนึ่งที่ผู้กำหนดนโยบายก็คือการสำรวจความคิดเห็นของสาธารณะ เพื่อให้ง่ายในการกำหนดนโยบาย
Structure:
Subject + have/ has + Past Participle (3rd Form of the Verb)
e.g. She has finished the letter.
สิ่งแวดล้อมทางสังคม
Present Continuous is used to indicate the ongoing time (now).
Some adverbs used with Present Continuous:
- now, right now
- at this moment
- at the moment
- continually
- perpetually
- this year
- this season
- forever
มีความสัมพันธ์กับองค์ประกอบของประชากร สร้างด้วยอายุ เชื้อชาติ เพศ และอื่น ๆ ซึ่งองค์ประกอบเหล่านี้จะเป็นอิทธิพลที่สำคัญในการกำหนดนโยบายสาธารณะ
Structure:
Subject + BE (am/is/are) + Verb-ING
e.g. You are eating now.
โครงสร้างทางสิ่งแวดล้อม
Present Simple is used for:
- habits
- general truths
- repeated actions of events
- fixed arrangements/timetables
- feelings/opinions/beliefs
- instructions.
Some adverbs used with Present Simple:
- always
- usually
- seldom
- never
- sometimes
- often
- frequently, generally
- habitually, occasionally
- once, twice
ในเวลาต่อมาได้อนุญาตให้ประชาชน
เข้าถึงรัฐบาลได้ ซึ่งทำให้ประชาชนช่วยสร้างรากฐานการปฏิบัติของ
รัฐบาล แต่ในทางกลับกันในการทำงานอาจมีความล่าช้า
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + do not / don’t + V1 (First Form of Verb)
Subject (He, She, It) + does not / doesn’t + V1 (First Form of Verb)
e.g. He doesn’t work in a bank.
โครงสร้างหลักเหล่านี้จะครอบคลุมไปด้วยการแบ่งแยกของอำนาจ
ไปสู่รัฐบาล ระบบของรัฐ และสหพันธรัฐ
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I usually go jogging at weekends.
Subject (He, She, It)+ V1(First Form of Verb) + s/es
e.g. She writes every day.