da Memoop 2cnu mancano 7 mesi
122
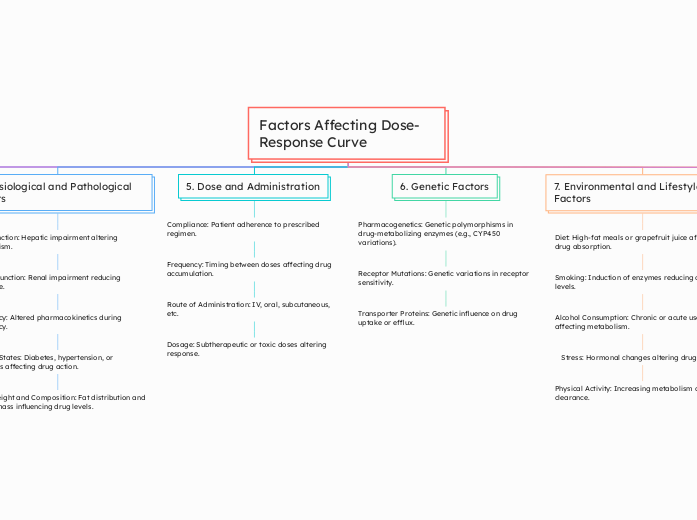
Factors Affecting Dose-Response Curve
da Memoop 2cnu mancano 7 mesi
122

Drug-Drug Delivery Systems: Nanocarriers or liposomes improving targeting.
Potency: Amount of drug needed to produce a specific effect.
Efficacy: Maximum effect achievable with the drug.
Particle Size: Smaller particles improving absorption.
Alcohol Consumption: Chronic or acute use affecting metabolism.
Stress: Hormonal changes altering drug effects.
Physical Activity: Increasing metabolism and clearance.
Transporter Proteins: Genetic influence on drug uptake or efflux.
Route of Administration: IV, oral, subcutaneous, etc.
Dosage: Subtherapeutic or toxic doses altering response.
Pregnancy: Altered pharmacokinetics during pregnancy.
Disease States: Diabetes, hypertension, or infections affecting drug action.
Body Weight and Composition: Fat distribution and muscle mass influencing drug levels.
Enzyme Inhibition: Drug inhibiting metabolic enzymes (e.g., CYP450
Enzyme Induction: Drug inducing metabolic enzymes.
Competitive Binding: Drugs competing for the same receptor.
Intrinsic Activity: Ability of the drug to activate the receptor.
Desensitization: Reduced receptor response with prolonged exposure.
Upregulation/Downregulation: Changes in receptor expression levels.
Metabolism: First-pass metabolism and active metabolites.
Drug Stability: Degradation under physiological conditions.
Excretion: Renal and biliary excretion.