von Leila Gatbonton Vor 6 Monaten
166
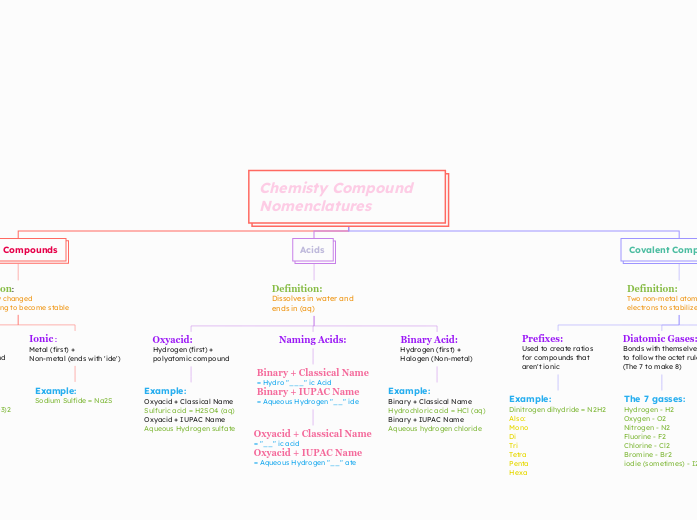
Chemisty Compound Nomenclatures
von Leila Gatbonton Vor 6 Monaten
166

Mehr dazu
HONC Rule: Tells us the combining capacity of atoms H - Hydrogen + Halogens (form 1) O - Oxygen + Sulfur (form 2) N - Nitrogen + Phosphorus (form 3) C - Carbon + Silicon (form 4)
The 7 gasses: Hydrogen - H2 Oxygen - O2 Nitrogen - N2 Fluorine - F2 Chlorine - Cl2 Bromine - Br2 iodie (sometimes) - I2
Example: Dinitrogen dihydride = N2H2 Also: Mono Di Tri Tetra Penta Hexa
Example: Binary + Classical Name Hydrochloric acid = HCl (aq) Binary + IUPAC Name Aqueous hydrogen chloride
Binary + Classical Name = Hydro "___" ic Acid Binary + IUPAC Name = Aqueous Hydrogen "__" ide
Oxyacid + Classical Name = "__" ic acid Oxyacid + IUPAC Name = Aqueous Hydrogen "__" ate
Example: Oxyacid + Classical Name Sulfuric acid = H2SO4 (aq) Oxyacid + IUPAC Name Aqueous Hydrogen sulfate
Example: Sodium Sulfide = Na2S
Example: Clacium Chlorate = Ca(ClO3)2