a harmanpreet kaur 3 éve
382
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS
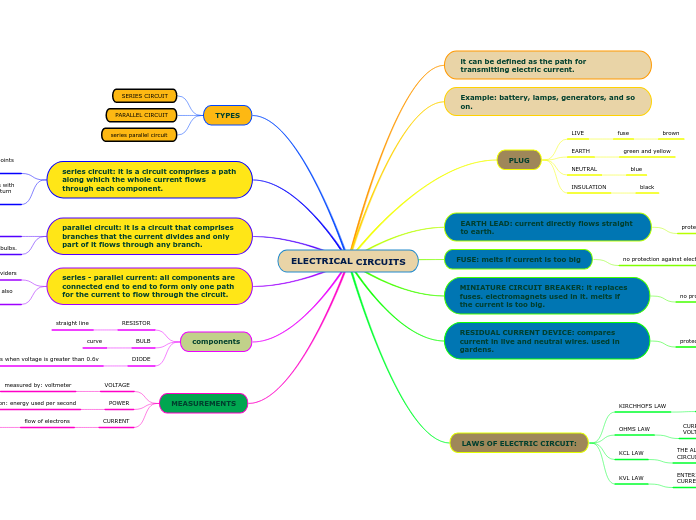
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS
MEASUREMENTS
CURRENT
flow of electrons
measured by: ammeter
units: ampere(A)
POWER
definition: energy used per second
units: watts(W)
VOLTAGE
measured by: voltmeter
connected in parallel
units: volts(V)
components
DIODE
current only flows when voltage is greater than 0.6v
BULB
curve
RESISTOR
straight line
series - parallel current: all components are connected end to end to form only one path for the current to flow through the circuit.
For example: multiple bulbs are connected with wire and also some are in the loop
used for: voltage dividers
parallel circuit: it is a circuit that comprises branches that the current divides and only part of it flows through any branch.
example: light fixtures that use multiple bulbs.
used for: to keep electricity flowing when one pathway is interrupted.
series circuit: it is a circuit comprises a path along which the whole current flows through each component.
examples: often lawnmowers have two switches in series with each other so both need to switch before the mower will turn on.
used for: it provides exactly one path between any two points for electric current.
TYPES
series parallel circuit
PARALLEL CIRCUIT
SERIES CIRCUIT
LAWS OF ELECTRIC CIRCUIT:
KVL LAW
ENTERING CURRENT AT NODE IS EQUAL TO LEAVING CURRENT AT NODE.
KCL LAW
THE ALGEBRAIC SUM OF VOLTAGE AT NODE IN A CLOSED CIRCUIT IS ZERO.
OHMS LAW
CURRENT THROUGH A CIRCUIT IS PROPORTIONAL TO THE VOLTAGE ACROSS THE CONDUCTOR
KIRCHHOFS LAW
RESIDUAL CURRENT DEVICE: compares current in live and neutral wires. used in gardens.
MINIATURE CIRCUIT BREAKER: it replaces fuses. electromagnets used in it. melts if the current is too big.
no protection against electric shock.
FUSE: melts if current is too big
no protection against electric shock
EARTH LEAD: current directly flows straight to earth.
protects against electric shocks
PLUG
INSULATION
black
NEUTRAL
blue
EARTH
green and yellow
LIVE
fuse
brown
Example: battery, lamps, generators, and so on.
it can be defined as the path for transmitting electric current.

