przez Katia Alvarez 6 lat temu
422
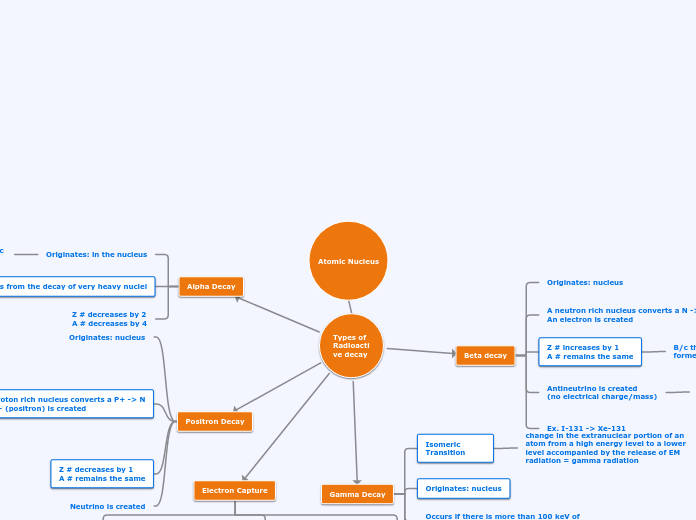
Atomic Nucleus Homework
przez Katia Alvarez 6 lat temu
422

Więcej takich
X-rays are emitted
when the e+ is created it looses energy b/c its colliding with surrounding matter, it gets attracted to an electron and they spiral towards one another before annihilation. (mass of the e+ and e- is converted into pure EM energy)
change in the extranuclear portion of an atom from a high energy level to a lower level accompanied by the release of EM radiation = gamma radiation
needed to conserve energy in the decay it carries away the difference between B- particle energy and the decay energy.
B/c the Z # changed, a new element is formed
alpha particles are monoenergetic range in matter is very short