przez Aguilera Gael 3 lat temu
277
Nomenclature
przez Aguilera Gael 3 lat temu
277

Więcej takich
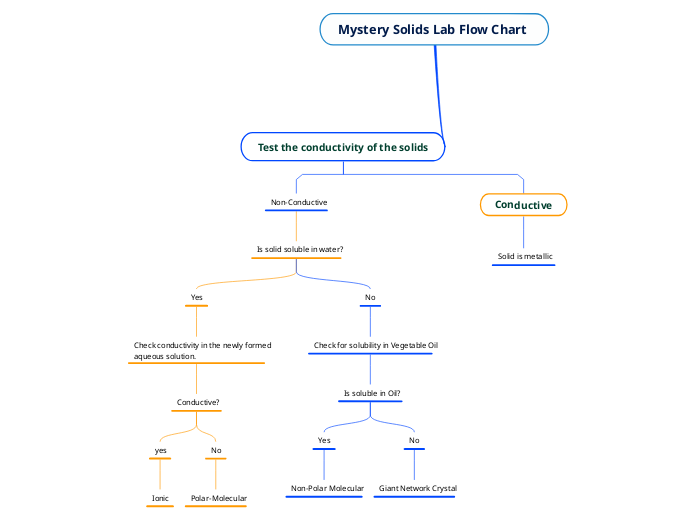

przez Musa Qureshi
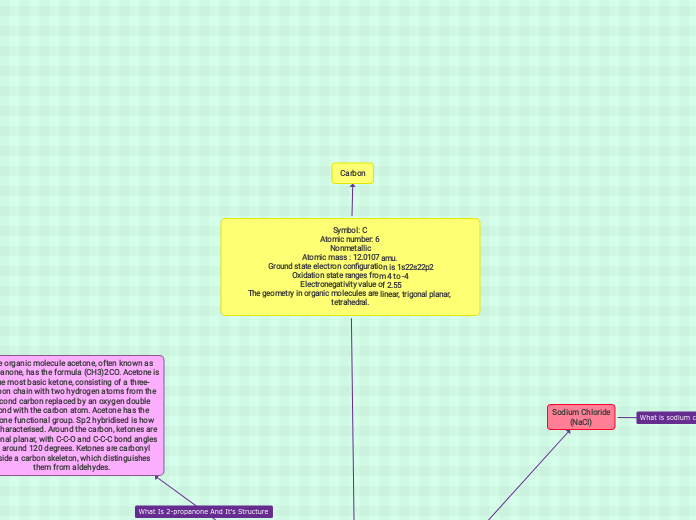

przez Shelby Williams

przez angie azuaje


przez anis suraya
Example
Example: Carbon Dioxide
Example: Octane
Example: Sodium Phosphide
If it's a multivalent un cross the numbers to get their charge they specify the multivalent metal by indicating it's charged by a roman numeral.
The noble gases are in a gaseous form at room temperature. There are seven of them, an example being neon. They have a complete outer shell, so they usually don't combine with other elements.
Are elements that gains electrons rather than losing them. Since they absorb electrons they become negatively charged as they have more electrons than protons. They are the anion of a bond, so they are named after the metal.They are on the right side of the periodic table.
A Multivalent Metal is a metal that could have different valence electrons. Indicate the number of valence electrons it has with a roman numeral. One for each valence electron.
Metals are elements that lose their electrons. And because they lose electrons they are positively charged as they now have more protons than electrons. They are the cation of a bond, so they are named before the metal. They are on the left side of the periodic table. With the exception of hydrogen which is a non-metal.
Diatomic elements are elements that can't exist on their own. Meaning that they must have two elements to exist. But it could be another one of itself though. Like Nitrogen, nitrogen is N2 because N1 cannot exist. But they can also bond with other elements to complete themselves, like Carbon Monoxide, as oxygen is a diatomic as well and uses the carbon to complete itself. And yes, this is a molecular bond, as they are both non-metals.
Molecular compounds are compounds that are not made up of a metal and non- metal. And they share electrons rather than losing or gaining them. They share their electrons since they are nonmetals.
Example: Water
They share electrons they don't lose or gain them.
Ionic basic
Basic Ionic compounds are the metals and non metals, which is the most simple kind of compound, and remember that you write the metal before the non-metal.
Ex. Sodium Chloride=NaCL
Multivalent
They are compounds that have metals that have more than one possible valence charge to them. Determine the charge before writing the formula by uncrossing the number of each element in the formula and indicate the multivalent metal by placing a roman numeral in front of it.
Ex. FeO=Iron(II) Oxide
Polyatomics
Polyatomic compounds are compounded with more than two atoms.Usually this is with oxygen. Such as chlorate, which is CLO3. When naming polyatomics, you add the suffix ate instead of -ide to indicate that it is polyatomic.
Ex.Phosphate= PO4
Is a compound created by a covalent bond when they share electrons. These are when you add the special endings on two the names of the compounds. Depending on the number of atoms it determines your prefix, that goes on both the metal and non-metal. You don't add a prefix if the first element has one though.
Prefixes
Ex. Carbon Dioxide CO2 Dihydrogen Oxide. H2O Fancy name for water.