realizată de Sharon Wong 7 ani în urmă
277
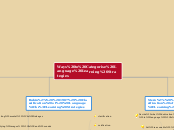
Ways to Categorise Language Learning Strategies
realizată de Sharon Wong 7 ani în urmă
277

Mai multe ca acesta
boday movement
a combination of sounds and images
images
sounds
make use of linguistic or communicative knowledge
clarifying what the speaker intends to say
getting meaning across
conversation
self- management
setting goals
prioritising
planning
monitoring
memorisation
practice
deductive reasonign
inductive inference
guessing
verification
clarification
empathising with others
cooperative with others
asking questions
regulating emotions
self-encouragement
lowering anxiety
evaluating own learning
arranging and planning own learning
centring own learning
overcoming difficulties in productive skills
guessing intelligently
creating structure for input and output
analysing and reasoning
receiving and sending messages
practising
employing action
reviewing well
applying images and sounds
creating mental linkages