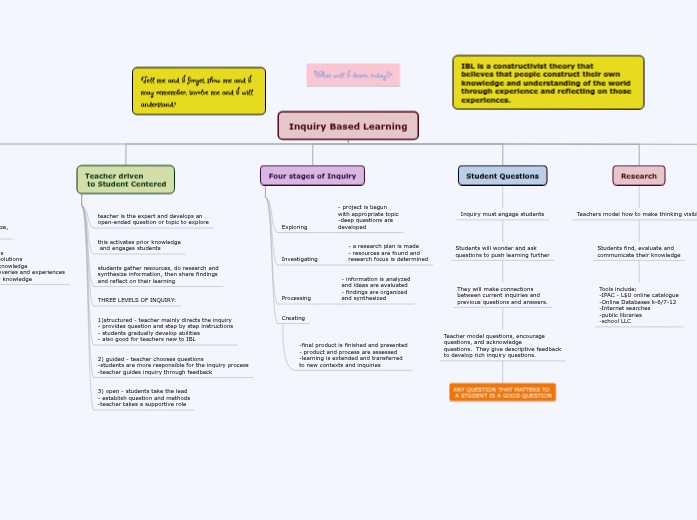
"What will I learn today?"
"Tell me and I forget, show me and I may remember, involve me and I will understand."
IBL is a constructivist theory that
believes that people construct their own knowledge and understanding of the world
through experience and reflecting on those
experiences.
Inquiry Based Learning
Importance of IBL
Actively involves students in
their own learning
Not passive learning
Encourages higher order thinking
Encourages curiosity and excitement
by providing a "spark" that traditional
methods may not.
Research
Teachers model how to make thinking visible
Students find, evaluate and
communicate their knowledge
Tools include:
-IPAC - L$U online catalogue
-Online Databases k-6/7-12
-Internet searches
-public libraries
-school LLC
Student Questions
Inquiry must engage students
Students will wonder and ask
questions to push learning further
They will make connections
between current inquiries and
previous questions and answers.
Teacher model questions, encourage
questions, and acknowledge
questions. They give descriptive feedback
to develop rich inquiry questions.
ANY QUESTION THAT MATTERS TO
A STUDENT IS A GOOD QUESTION
Four stages of Inquiry
Creating
-final product is finished and presented
- product and process are assessed
-learning is extended and transferred
to new contexts and inquiries
Processing
- information is analyzed
and ideas are evaluated
- findings are organized
and synthesized
Investigating
- a research plan is made
- resources are found and
research focus is determined
Exploring
- project is begun
with appropriate topic
-deep questions are
developed
Teacher driven
to Student Centered
3) open - students take the lead
- establish question and methods
-teacher takes a supportive role
2) guided - teacher chooses questions
-students are more responsible for the inquiry process
-teacher guides inquiry through feedback
1)structured - teacher mainly directs the inquiry
- provides question and step by step instructions
- students gradually develop abilities
- also good for teachers new to IBL
THREE LEVELS OF INQUIRY:
students gather resources, do research and
synthesize information, then share findings
and reflect on their learning
this activates prior knowledge
and engages students
teacher is the expert and develops an
open-ended question or topic to explore
Theory of IBL
Steps:
- ask questions
- investigate solutions
- create new knowledge
- discuss discoveries and experiences
reflect on new knowledge
students learn skills to synthesize,
interpret and evaluate
NOT teacher directed