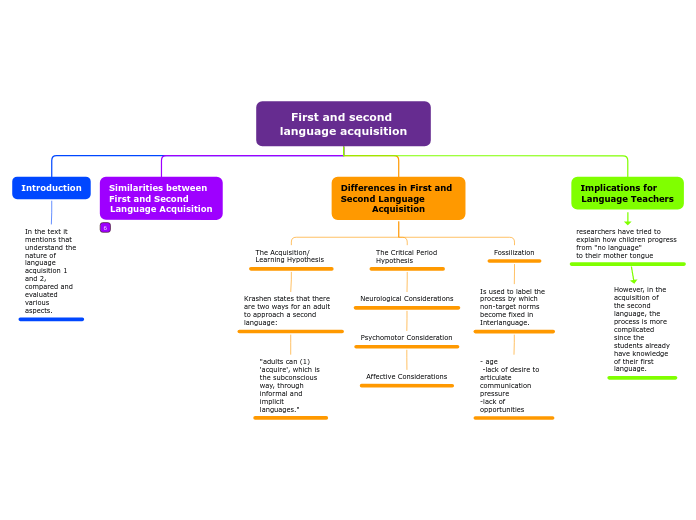
First and second language acquisition
Implications for Language Teachers
researchers have tried to explain how children progress from "no language"
to their mother tongue
However, in the acquisition of the second language, the process is more complicated since the students already have knowledge
of their first language.
Differences in First and Second Language Acquisition
Fossilization
Is used to label the process by which non-target norms become fixed in Interlanguage.
- age
-lack of desire to articulate communication pressure
-lack of opportunities
The Critical Period Hypothesis
Neurological Considerations
Psychomotor Consideration
Affective Considerations
The Acquisition/ Learning Hypothesis
Krashen states that there are two ways for an adult to approach a second language:
"adults can (1) 'acquire', which is the subconscious way, through informal and implicit languages."
Similarities between First and Second Language Acquisition
2.1 Developmental Sequences
2.2 Acquisition Order
2.3 Linguistic Universals and Markedness
2.4 Input
2.5 Behavioristic Views of Language Acquisition
2.6 Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD)
Introduction
In the text it mentions that
understand the nature of language acquisition 1 and 2, compared and evaluated various aspects.