by Doris Cruz 6 years ago
1023
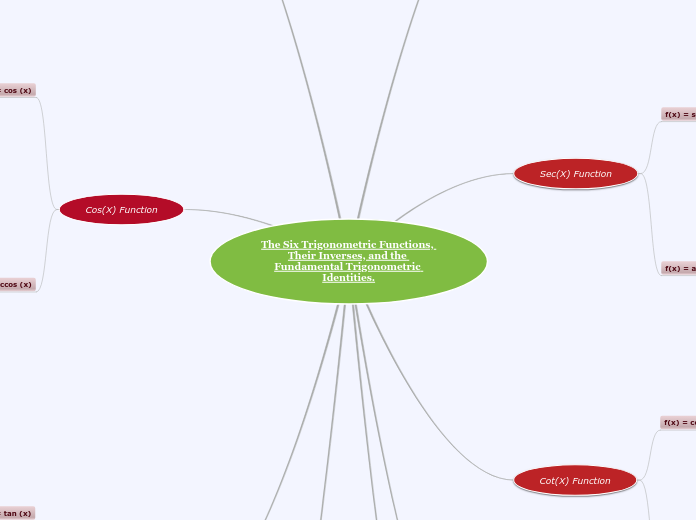
A Must Know in Trigonometry
by Doris Cruz 6 years ago
1023

More like this
Range: (−π/2,π/2)
Range: all real numbers
Domain: all real numbers except pi/2 + k pi, k is an integer.
Range: [0,π]
Range: [-1 , 1]
Range: [−π/2,π/2]
Domain: [−1,1]
Period = 2pi
Range: [-1 , 1]
Domain: all real numbers
Subtopic
Astmtote: y=pi/4; 17pi/4
Range: (0,π)
Domain: (−∞,∞)
Period = pi
Range: all real numbers
Domain: all real numbers except k pi, k is an integer
Domain: all real numbers except k pi, k is an integer
Asymptote: y = -pi
Range: [0,π/2)∪(π/2,π]
Vertical asymptotes: x = pi/2 + k pi, where k is an integer.
Period = 2 pi
Range: (-infinity , -1] U [1 , +infinity)
Domain: all real numbers except pi/2 + k pi, n is an integer
Asymtote: y= -pi
Range: [−π/2,0)∪(0,π/2]
Domain: (−∞,−1]∪[1,∞)
Properties
Vertical asymptotes: x = k pi, where k is an integer.
Period = 2pi
Range: (-infinity , -1] U [1 , +infinity)
Domain: all real numbers except k pi, k is an integer.