by Mindomo Team 2 years ago
639831
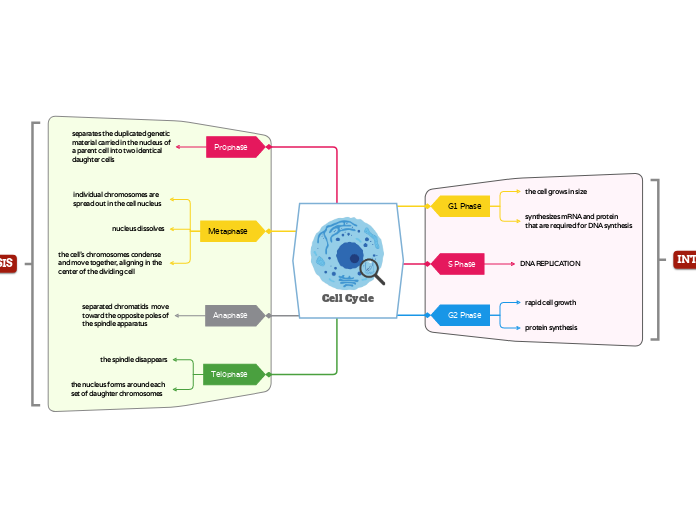
Cell Cycle
Mitosis is a process of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells. It is a part of the broader cell cycle, which includes several phases. During interphase, the cell prepares for division by growing in size and replicating its DNA.