fluids
fluids under pressure
laws
pressure
can be
exerted by
the mass
of the fluids
around you
pressure lower
and lower
will increase
because there
is more fluids
above you,
and thus more
mass
pascal's law states
that a force that
operates on a
fluid is felt equally
throughout the
mass
application
we apply these
systems and
laws daily to
make our lives
better, but it
must also be
used with
responsibility,
as it can hurt
the environment
Hydraulic and
pneumatic
systems, as
well as
models
demonstrating
pascal's law
use syringes,
tubing, water,
and air
difference between
liquids and gasses
liquids tend to
be more dense
than their gas
counterparts
liquids make
hydraulic systems
and gasses make
pneumatic systems
liquids are less
compressible
than gasses
density and buoyancy
it can be applied
to do things that
relate to fluids
an example of
an application
of this is a
hydrometer,
which will
measure the
density of a
fluid
buoyancy
an example of this
is a fish's swim
bladder, which
will fill up with
water to sink and
will be empty to
rise
buoyancy is a
force that
apposes gravity
created by fluids
and acts on objects
the buoyant force
is the force that
pushes an object
up if it is less
dense than the
fluid it is
suspended in
quantities
all of these measures
can be measured, as
all matter has these
intrinsic properties
Density is the
measure of
mass per unit
volume
volume is the
amount of 3
dimensional
space an
object takes
mass is the
amount of
matter in an
object
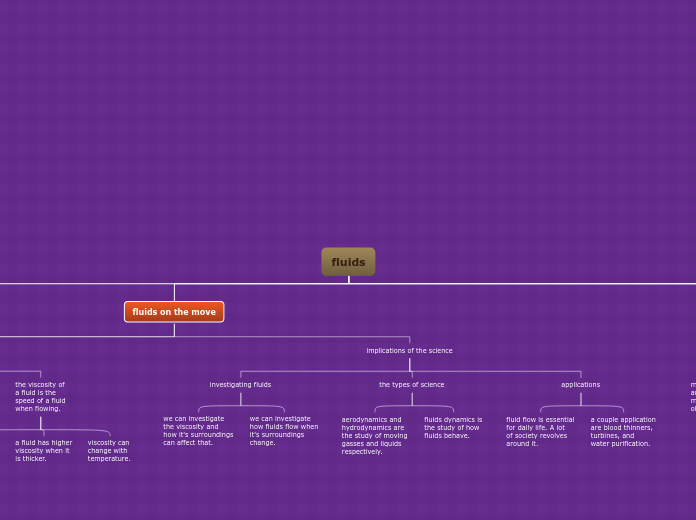
fluids on the move
implications of the science
applications
a couple application
are blood thinners,
turbines, and
water purification.
fluid flow is essential
for daily life. A lot
of society revolves
around it.
the types of science
fluids dynamics is
the study of how
fluids behave.
aerodynamics and
hydrodynamics are
the study of moving
gasses and liquids
respectively.
investigating fluids
we can investigate
how fluids flow when
it's surroundings
change.
we can investigate
the viscosity and
how it's surroundings
can affect that.
fluid flow
the viscosity of
a fluid is the
speed of a fluid
when flowing.
viscosity can
change with
temperature.
a fluid has higher
viscosity when it
is thicker.
viscosity is also
a measure of
how thick or
thin a fluids is
fluids can have
laminar or
turbulent flow.
laminar=smooth flow
turbulent=rough flow
fluids come in many forms
i.e. water is a liquid and
air is a gas
properties
fluids have no
definite shape.
definitions
extra things
I couldn't fit
in the rest
of this
organigram
to streamline is
to make
an object that
will have a
natural higher
resistance to
friction with
fluid particles,
such as a design
for a boat that
will cut through
water
surface tension
is a strong
cohesion of
particles on the
surface of a
fluid
valves regulate
and modulate
the flow of fluids
in a system, like
in tubing
atmospheric
pressure is
caused by
the mass
of the
atmosphere
above you
adhesion and
cohesion is a
force between
particles of 2
different
objects and
the strength
of that force
respectively
main idea's
life is impossible
without fluids
fluids have a myriad
of different properties
fluids are very
important.
Liquids are the state just next to solids,
having some potential energy as kinetic
energy between the molecules of the
substance. It will move to fit it's
container. Gas, on the other hand, will
take up the most space and the least
density. Unlike most liquids, gasses are
compressible.