przez Lorena cuesta palacios 3 lat temu
211
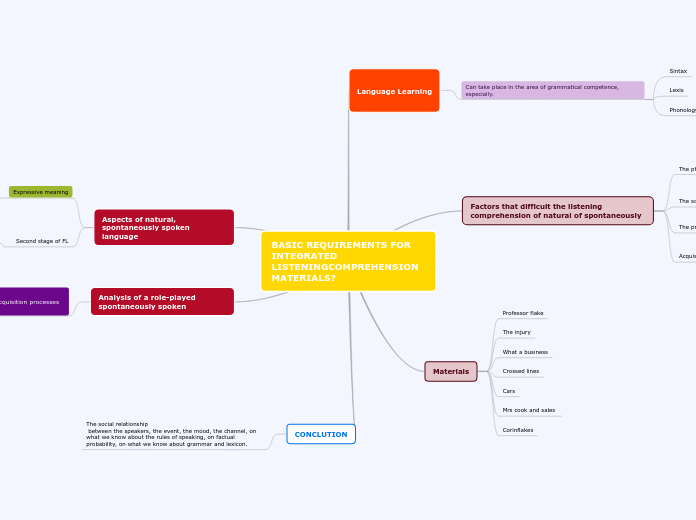
BASIC REQUIREMENTS FOR INTEGRATED LISTENINGCOMPREHENSION MATERIALS?
przez Lorena cuesta palacios 3 lat temu
211

Więcej takich
Non verbal communication
According to von Raffler-Engel
Kinesics
Social Mobements
Body-Language
Unconscious acquisition processes
A receptive competition of this sociolinguistic variation is a second learning objective of listening comprehension