przez shakira rahma 4 lat temu
426
History IPS. 🌏
przez shakira rahma 4 lat temu
426

Więcej takich
Sumber sekunder dapat berupa: buku teks, koran, majalah, ensiklopedi, tinjauan penelitian, dan referensi-referensi lain
Sumber primer dapat berupa keterangan langsung dari: pelaku dan saksi sejarah, dokumen asli laporan atau catatan, foto, benda peninggalan, film, artefak
Kedekatan emosional adalah hubungan pribadi antara peneliti dengan objek yang ditelitinya. Misalnya: seorang peneliti yang lahir dan tinggal di Jakarta akan lebih bagus menulis sejarah kota Jakarta daripada peneliti yang tinggal di luar kota.
METODE SEJARAH proses menguji dan menganalisa secara kritis sumber sejarah dan peninggalan masa lampau dalam rangka menghasilkan gambaran yang benar tentang peristiwa itu.
Along with mass production of steel tools and weapons, the age saw even further advances in architecture, with four-room homes, some complete with stables for animals, joining more rudimentary hill forts, as well as royal palaces, temples and other religious structures. Early city planning also took place, with blocks of homes being erected along paved or cobblestone streets and water systems put into place.
Agriculture, art and religion all became more sophisticated, and writing systems and written documentation, including alphabets, began to emerge, ushering in the Early Historical Period.
This time period also brought advances in architecture and art, including the invention of the potter’s wheel, and textiles—clothing consisted of mostly wool items such as skirts, kilts, tunics and cloaks. Home dwellings morphed to so-called roundhouses, consisting of a circular stone wall with a thatched or turf roof, complete with a fireplace or hearth, and more villages and cities began to form.
Organized government, law and warfare, as well as beginnings of religion, also came into play during the Bronze Age, perhaps most notably relating to the ancient Egyptians who built the pyramids during this time. The earliest written accounts, including Egyptian hieroglyphs and petroglyphs (rock engravings), are also dated to
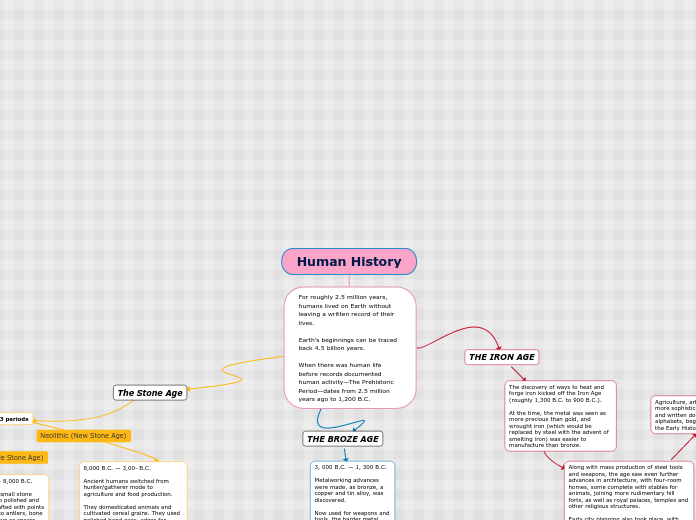
8,000 B.C. — 3,00- B.C. Ancient humans switched from hunter/gatherer mode to agriculture and food production. They domesticated animals and cultivated cereal grains. They used polished hand axes, adzes for ploughing and tilling the land and started to settle in the plains. Advancements were made not only in tools but also in farming, home construction and art, including pottery, sewing and weaving.
10,000 B.C. — 8,000 B.C. Humans used small stone tools, now also polished and sometimes crafted with points and attached to antlers, bone or wood to serve as spears and arrows. They often lived nomadically in camps near rivers and other bodies of water. Agriculture was introduced during this time, which led to more permanent settlements in villages.
2.5 million years ago to 10,000 B.C. Humans lived in caves, huts, tepees. Humans were hunters and gatherers. They used basic stone and bone tools, as well as crude stone axes, for hunting birds and wild animals. They cooked their prey, including woolly mammoths, deer and bison, using controlled fire. They also fished and collected berries, fruit and nuts.
Ancient humans in the Paleolithic period were also the first to leave behind art. They used combinations of minerals, ochres, burnt bone meal and charcoal mixed into water, blood, animal fats and tree saps to etch humans, animals and signs. They also carved small figurines from stones, clay, bones and antlers.
The end of this period marked the end of the last Ice Age, which resulted in the extinction of many large mammals and rising sea levels and climate change that eventually caused man to migrate.