-STAGES OF THE PROJECT APPROACH-
pagina 24
EVALUATION
REPORT:
-Description of,
the prototype built, list of modifications made, final drawing of the solution, total cost of the proyect, envirormental impact of the solution created, your own thoughts about how the work went.
Once we have built the prototype,
we must test it to know if its works perfectly.We also have to check the production proccess and planing by reflecting how we could improve the design and by gathering rimpression from the potential users or the product.
BUILDING
Procces shit: we use this document to record the progress of the stages of our work each day. We describe the completed tasks and the names of the people in charge of them, the difficulties we encountred and any changes or modifications that we add to make.We can also created a construction log.
Is the drawing, the list of materials
and tools and the budget are all included in the initial planing for developing prototype.
SEARCH FOR INFORMATION.PRODUCT ANALYSIS.POSIBLE SOLUTIONS.
HISTORICAL
ANALYSIS
We evaluate the possible
reasons why the object
emerged and its historical
development. We also
analyse its possible future
development.
AESTHETIC
ANALYSIS
We evaluate how our
senses react to the object,
its appearance,whether it
looks nice or not, whether
we find it attractive etc.
This analysis is very important
for some objects because
the appearance of the product
could motivate a potential
buyer to purchase it.
SOCIAL
ANALYSIS
We study the object
from the point of view
of its social impact and
analyse the human needs
that it meets. We also
evaluate its environmental
impact and recyclability.
ECONOMIC
ANALYSIS
We analyse the financial cost
of manufacturing the product and its selling price. We study wheter the material and manufacturing procedures udes are cheap or wheter they make the product more expensive. We determinate wheter the selling price of the object is correct by comparing it to similar objects.
TECHNICAL
ANALYSIS
We study how the object is made.
This analysis includes the study of its materials, the technology used to make it , how its parts are joined thogeter and the envirormental risks of the material used.
FUNCTIONAL
ANALYSIS
We study how the object
works, its utility how it
is used and the potential
risks of its use. In more
complicated objects, we
also analyse the function
of each part of the object.
MORPHOLOGICAL
ANALYSIS
We analyse the shape of the object,
its size, colour and basic physical
characteristicas.For this, we use drawings
of the complete object and exploded views of its parts. Sometimes, we also study its ergonomic characteristics to evaluate how suituable it is for humans.
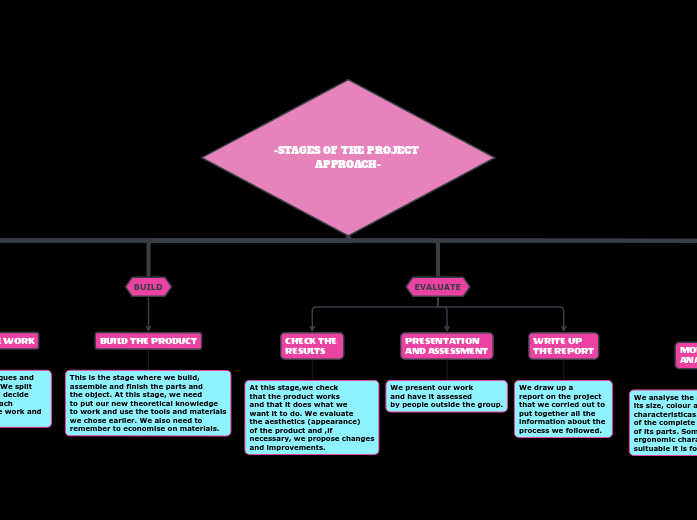
EVALUATE
WRITE UP
THE REPORT
We draw up a
report on the project
that we corried out to
put together all the
information about the
process we followed.
PRESENTATION
AND ASSESSMENT
We present our work
and have it assessed
by people outside the group.
CHECK THE
RESULTS
At this stage,we check
that the product works
and that it does what we
want it to do. We evaluate
the aesthetics (appearance)
of the product and ,if
necessary, we propose changes
and improvements.
BUILD
BUILD THE PRODUCT
This is the stage where we build,
assemble and finish the parts and
the object. At this stage, we need
to put our new theoretical knowledge
to work and use the tools and materials
we chose earlier. We also need to
remember to economise on materials.
DESIGN
PREPARE AND PLAN THE WORK
We choose the materials, techniques and tools that we are going to need. We split the work up into small tasks and decide how long we need to spend on each operation. We then share out the work and put the blocks of work in order.
We do drawings (sketches) and diagrams or plans of our chosen solutions. We can do these freehand first and add more details later, but we must make sure that the product is aesthically pleasing.
ANALYSE
CHOOSE THE SOLUTION
We choose the best solution based on the criteria that we set as priorities(type of materials, size, shape, cost..)and afteranalysing the advantage and disadvantages of each solutions.
SEARCH FOR
POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS
We think of the different options, i.e. different objects or products that could resolve the problem. We study and asses each option to see if it is viable.
INFORMATIO AND
RESEARCH
We collate, study and select informationon the different ways that we could resolve the problem. We also study products that meet similar needs.
DETECT THE
PROBLEM OR NEED
What do we need? What problem do we have or what task hae we been set? What conditions are there? If we are very clear about the problem we need to resolve and we know all the details, the rest of the procces will be easier.
THE PROJECT APPROACH:
DESIGN
Once we have done our analysis,
and depending on the conditioning
factors of each problem, we can propose different solutions .We then need to select the best
solution for our needs.
We must be objective when we choose our solution by checking whether the product meets our requirements, whether it is easy to build and whether the materials that we need are affordable and easy to find.
DESIGN:
The design stage is especially
important because this is when we define all the features of the solution: not only its form and appearance but also the cost of its production and the
distribution of tasks to build it .
THECHNICAL DOCUMENTS:
BUDGET:
The budget is the document
that we use to evaluate the
financial cost our solution.
In the workshop, the materials
that we use are not very expensive;
however in companies, the budget is
crucial for deciding whether or not
to build a prototype.
Spreadsheets are very useful
for creating budgets. In them,
we must include the real cost of
all of the real cost of all of the
components and all applicable
taxes. When you create the budget
for building your prototype, you
will probably be surprised by the total cost.
LIST OF MATERIALS
AND TOOLS:
Once we have designed
our solution, it is very important
to list all the materials that we will
need to build it. Take your time and
plan properly. Sometimes a material
we need may not be available and we
have to order it. This can delay the construction of the prototype
Your list of materials should not be a
vague list; it should contain each element
that we need and the correct amounts of
each one. Instead of ordening "lamps, we
should order "three 3V lamps". If our list of
materials is accurate, our planning will be more affective.
DRAWINGS:
Drawings show how
the object we are going
to build will look. Usually,
there will be one general
drawing of the object and
other drawings of its
different parts or sections.
Perspectives and views
are often used and the
necessary measurements
and details are added to the drawins.