por Qabas Al-Jobori 1 ano atrás
86
Babalola Headaches
por Qabas Al-Jobori 1 ano atrás
86

-Naproxen 550mg BID -Frovatriptan BID or Nara/zolm as alts. -Candesartan -Lisinopril
Cautions
Galcanezumab: AVOID in pts w/ CVD or recent CV event
Fremanezumab: AVOID in pts w/ CVD or thromboembolic events
Eptinezumab: AVOID in pts w/ CVD
Atogepant: -AVOID in severe hepatic impairment -reduce dose w/ severe or ESR impairment
ADEs:
-Atogepant -Rimegepant -Eptinezumab -Erenumab -Fremanezumab -Galcanezumab
ADEs: -Drowsiness/fatigue -sleep disturb -vivid dreams 👻 -memory disturbance -depression -bradycardia -hypotension
MOA: -raise migraine threshold via adrenergic/serotonergic modulation
Metoprolol, Propranolol, Timolol
Ven: Risk of serotonin syndrome if combined w/ other agents
Ami: AVOID in pts w/ glaucoma. BPH, recent MI
ADEs: -Ami: anticholinergic effects, inc appetite, weight gain, sedation, ortho hypotension, slow AV conduction -Ven: N/V, drowsiness
MOA: -downregulation of central 5-HT -inc synaptic norepinephrine -enhance opioid receptor action
Amitriptyline Venlafaxine
Topiramate: -Avoid in history of kidney stones or cog impairment
Diva: -CI in pregnancy, women of child-bearing age not on contraception -BOXED WARNING: pancreatitis, hepatotoxicity
ADEs: -Diva: alopecia, weight gain, tremors, nausea, hepatotoxicity -Topiramate: paresthesia, fatigue, anorexia, diarrhea, weight loss
Remember that Diva Val got pregnant (gained weight)
+
find a Top zaddy when I lose weight
MOA: -enhance GABA inhibition -Mod excitatory glutamate -inhibit Na/Ca channel activity
-Valproate -Divalproex -Topiramate
DDIs: -SSRI, SNRI, TCA, MAOIs, etc (Serotonin syndrome) -Avoid other CNS depressants -Heart rate lowering meds (monitor/caution)
Do NOT drive or operate heavy machinery w/in 8hrs of use
ADEs: -Dizziness -fatigue/sedations -parasthesia -N/V -Muscle weakness
MOA: Bind to 5-HT1F receptor
Lasmiditan (C-V)
-2nd line for mod-severe --use when contraindication for triptan or inadeq response to >+2 oral triptans
Acute txtm: -Ubro: ONLY for acute treatment -Rime: ALSO for prevention
DDIs: -CYP3A4 inhibitors/inducers -Rime: P-gp inhibitors/2nd dose w/in 48hrs -Ubro: BCRP/P-gp inhibitors, decrease dose
Cautions: -Rime: Avoid in child-push C, ESRD -Ubro Avoid ESRD, dec dose in severe renal/hepatic impairment
ADEs: -Rime: N, abdom pain, hypersensitivity -Ubro: N, somnolence, dry mouth
Rimegepant Ubrogepant
-2nd line for mod-severe sxs -use when contraindication for triptan or inadeq response to >+2 oral triptans
Fomulations: -oral absorption erratic/consider other forms -ergot combined w/ caffeine to enhance absorption + longer analgesia
Contraindications: -Hepatic failure -Coronary/cerebral/peripheral VD -Uncontrolled HTN -sepsis -pregnancy/nursing - strong CYP3A4 inhibitors -avoid w/in 24hrs of triptans
ADEs: -N/V -Abdom pain - fatigue/weak -parasthesias -muscle pain -diarrhea -chest tightness -ergotism
MOA: -Non-selec 5-HT1 agonist -constrict blood vessels -inhibit inflammation -dopa agonist -constrict arteries + veins
-Ergotamine tartrate -Dihydroergotamine
-1st option for acute treatment of mod-severe
Considerations
DDI: -Avoid w/i 24hrs of ergotamine derivatives -SSRIs/SNRIs (serotonin syndrome) -Avoid w/i 2 weeks of MAOIs (Suma, Riza, Almo, Zolm) - Avoid CYP3A4 inhibitors w/i 72hrs (Ele)
Caution: -Unspecified coronary artery disease -postmenopausal women -men >40yo -uncontrolled CV risk factors
Contraindication: -IHD, uncontrolled HTN -cerebrovasc disease -hemiplegic/basilar migraines
ADEs: -Dizziness 😵💫 - fatigue 😪 - Flushing -Parathesias - N/V 🤢 🤮 - Injection site rxn - taste perversion or nasal discomfort - chest/neck/throat pain
MOA: -Agonist of 5-HT1B/1D -normalize dilated intracranial arteries -inhibit vasoactive peptide release -inhibit transmission thru 2nd order neurons
-Suma -Zolmi -Nara -Riza -Almo -Frova -Ele
-1st line for acute treatment of mod-severe -Variable time to relief, typically 2hrs -inconsistent evd. of switching agents
Considerations:
Aspirin: -Tinnitus
Acetaminophen: -⚠️ hepatic dysfunction
NSAIDs: -inc BP, GI upset/bleed, dec kidney func - ⚠️ CVD
Likely effective: -Ketorolac (IV/IM) -Flurbiprofen -Ketoprofen
Efficacious agents: CANADIA -Aspirin -Celexocib -Diclofenac -Ibuprofen -Naproxen -Acetaminophen/aspirin/caffeine
MOA: inhibit prostaglandin synthesis -> prevention of inflammation
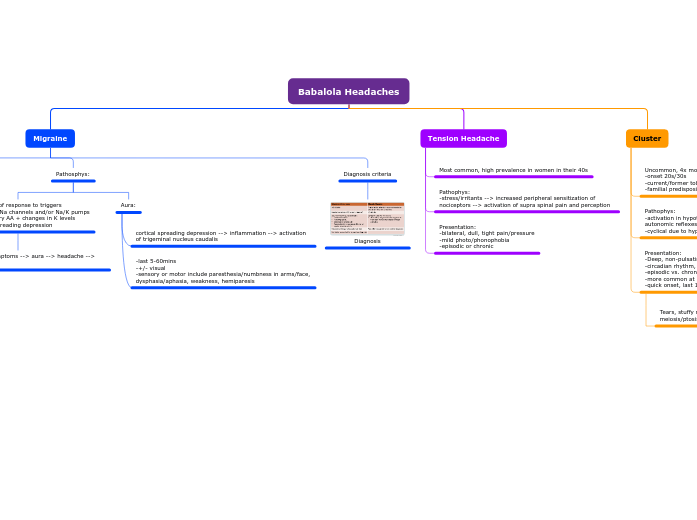
-last 5-60mins -+/- visual -sensory or motor include paresthesia/numbness in arms/face, dysphasia/aphasia, weakness, hemiparesis
cortical spreading depression --> inflammation --> activation of trigeminal nucleus caudalis
Phases: premonitory symptoms --> aura --> headache --> postdrome
4 phases of a migraine headache
Reasons for referral: -Systemic illness -focal neurological symptoms or papilledema -onset after 50yo -acute onset of first or worst headache ever -accelerating pattern of headache following subacute onset -secondary: cancer or HIV
Presentation: -4-72 hrs -unilateral, throbbing pain -GI sxs -sensory hyperacidity
Postdrome: AKA resolution of headache -tired, exhausted, irritable -depression/malaise -refreshed and euphoric