по christophe Mias 12 месяца назад
1519
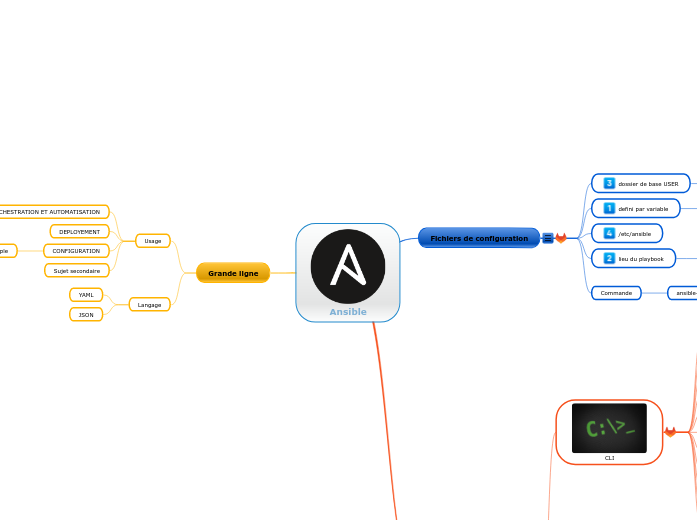
Ansible
по christophe Mias 12 месяца назад
1519

Больше похоже на это
Path multiple
répertoires associés
├── 00_inventory.yml├── group_vars│ ├── all.yml│ ├── dbserver.yml│ └── webserver│ ├── vault.yml│ └── webserver.yml└── host_vars ├── srv1 │ └── srv1.yml └── srv2.ymlhost_vars
group_vars
├── dev│ ├── 00_inventory.yml│ ├── group_vars│ │ ├── all.yml│ │ ├── dbserver.yml│ │ └── webserver│ │ ├── vault.yml│ │ └── webserver.yml│ └── host_vars│ ├── srv1│ │ └── srv1.yml│ └── srv2.yml├── prod│ ├── 00_inventory.yml│ ├── group_vars│ │ ├── all.yml│ │ ├── dbserver.yml│ │ └── webserver│ │ ├── vault.yml│ │ └── webserver.yml│ └── host_vars│ ├── srv1│ │ └── srv1.yml│ └── srv2.yml└── stage ├── 00_inventory.yml ├── group_vars │ ├── all.yml │ ├── dbserver.yml │ └── webserver │ ├── vault.yml │ └── webserver.yml └── host_vars ├── srv1 │ └── srv1.yml └── srv2.yml on retrouve cette structure dans la sortie de ansible-config, ex:
ansible -i "node2," all -b -e "var1=xavki" -m debug -a 'msg={{ var1 }}'
Inventaire dynamique
Documentation :
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/plugins/inventory.html
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/dev_guide/developing_inventory.html
https://github.com/ansible-collections/community.general/tree/main/scripts/inventory
ex: nmap.yml
plugin: nmap strict: false address: 172.17.0.0/24
récupération de l(inventaire
samik@Abacus:~/ansible_dir(abacustraining⚡) » ansible-inventory -i nmap.yml --list -y --output test.yml samik@Abacus:~/ansible_dir(abacustraining⚡) » cat test.yml all: children: ungrouped: hosts: node1: ip: 172.17.0.2 nginx_port: 8888 ports: - port: '22' protocol: tcp service: ssh state: open var1: groupvar node2: ip: 172.17.0.3 nginx_port: 8888 ports: - port: '22' protocol: tcp service: ssh state: open var1: groupvar node3: ip: 172.17.0.4 nginx_port: 8888 ports: - port: '22' protocol: tcp service: ssh state: open var1: groupvar node4: ip: 172.17.0.5 nginx_port: 8888 ports: - port: '22' protocol: tcp service: ssh state: open var1: groupvar
ansible -i nmap.yml all -m ping
[WARNING]: Platform linux on host node3 is using the discovered Python interpreter at
/usr/bin/python3.7, but future installation of another Python interpreter could change this. See
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/2.9/reference_appendices/interpreter_discovery.html for more
information.
node3 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3.7"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
[WARNING]: Platform linux on host node4 is using the discovered Python interpreter at
/usr/bin/python3.7, but future installation of another Python interpreter could change this. See
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/2.9/reference_appendices/interpreter_discovery.html for more
information.
node4 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3.7"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
...
inventory généré
ansible-inventory -i nmap.yml --list
{
"_meta": {
"hostvars": {
"node1": {
"ip": "172.17.0.2",
"nginx_port": 8888,
"ports": [
{
"port": "22",
"protocol": "tcp",
"service": "ssh",
"state": "open"
}
],
"var1": "groupvar"
},
"node2": {
"ip": "172.17.0.3",
"nginx_port": 8888,
"ports": [
{
"port": "22",
"protocol": "tcp",
"service": "ssh",
"state": "open"
}
],
"var1": "groupvar"
},
"node3": {
"ip": "172.17.0.4",
"nginx_port": 8888,
"ports": [
{
"port": "22",
"protocol": "tcp",
"service": "ssh",
"state": "open"
}
],
...
"var1": "groupvar"
},
"node4": {
"ip": "172.17.0.5",
"nginx_port": 8888,
"ports": [
{
"port": "22",
"protocol": "tcp",
"service": "ssh",
"state": "open"
}
],
"var1": "groupvar"
}
}
},
"all": {
"children": [
"ungrouped"
]
},
"ungrouped": {
"hosts": [
"node1",
"node2",
"node3",
"node4"
]
les différents plugins par défaut sont à configurer ici:
* ansible.cfg
[inventory] # enable inventory plugins, default: 'host_list', 'script', 'auto', 'yaml', 'ini', 'toml' #enable_plugins = host_list, virtualbox, yaml, constructed
le fichier de base
inventory.json
Inventory.yml
hosts
commande
ansible-inventory
--graph
--list
--toml
ajout de l'option avec:
--yaml
command line values (eg “-u user”) role defaults [1] inventory file or script group vars [2] inventory group_vars/all [3] playbook group_vars/all [3] inventory group_vars/* [3] playbook group_vars/* [3] inventory file or script host vars [2] inventory host_vars/* [3] playbook host_vars/* [3] host facts / cached set_facts [4] play vars play vars_prompt play vars_files role vars (defined in role/vars/main.yml) block vars (only for tasks in block) task vars (only for the task) include_vars set_facts / registered vars role (and include_role) params include params extra vars (always win precedence)Objectif : série de vidéo de mise en pratique autour du monitoring
prometheus / grafana / node-exporter...
* travail sur 4 noeuds
1- un de monitoring (prometheus/grafana)
2- tous monitoré par node exporter
* structure = inventory + playbook + role node exporter
Informations des conteneurs :
=> /samik-debian-4 - 172.17.0.5
=> /samik-debian-3 - 172.17.0.4
=> /samik-debian-2 - 172.17.0.3
=> /samik-debian-1 - 172.17.0.2
- name: Install Nodeexporter
hosts: all
become: yes
roles:
- node-exporter
- name: Install prometheus grafana
hosts: monito
become: yes
roles:
- monito
- grafana
phase3
role grafana
---
# handlers file for roles/grafana
- name: restart_grafana
systemd:
name: grafana-server
state: restarted
enabled: yes
daemon_reload: yes
dashboard-node-exporter.yml.j2
apiVersion: 1
providers:
- name: 'node-exporter'
orgId: 1
folder: ''
type: file
disableDeletion: false
updateIntervalSeconds: 10
options:
path: /var/lib/grafana/node-exporter.json
---
# tasks file for roles/grafana
- name: install gpg
apt:
name: gnupg,software-properties-common
state: present
update_cache: yes
cache_valid_time: 3600
- name: add gpg hey
apt_key:
url: "https://packages.grafana.com/gpg.key"
validate_certs: no
- name: add repository
apt_repository:
repo: "deb https://packages.grafana.com/oss/deb stable main"
state: present
validate_certs: no
- name: install grafana
apt:
name: grafana
state: latest
update_cache: yes
cache_valid_time: 3600
- name: change admin user
lineinfile:
path: /etc/grafana/grafana.ini
regexp: "{{ item.before }}"
line: "{{ item.after }}"
with_items:
- { before: "^;admin_user = admin", after: "admin_user = {{ grafana_admin_user }}"}
- { before: "^;admin_password = admin", after: "admin_password = {{ grafana_admin_password }}"}
notify: restart_grafana
- name: start service grafana-server
systemd:
name: grafana-server
state: started
enabled: yes
- name: wait for service up
uri:
url: "http://127.0.0.1:3000"
status_code: 200
register: __result
until: __result.status == 200
retries: 120
delay: 1
- name: add prometheus datasource
grafana_datasource:
name: "prometheus-local"
grafana_url: "http://127.0.0.1:3000"
grafana_user: "{{ grafana_user_admin }}"
grafana_password: "{{ grafana_admin_password }}"
org_id: "1"
ds_type: "prometheus"
ds_url: "127.0.0.1:9090"
changed_when: false
- name: install node exporter dashboard
get_url:
url: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rfrail3/grafana-dashboards/master/prometheus/node-exporter-full.json
dest: /var/lib/grafana/node-exporter.json
mode: '0755'
- name: activate dashboard for node exporter
template:
src: dashboard-node-exporter.yml.j2
dest: /etc/grafana/provisioning/dashboards/dashboard-node-exporter.yml
mode: 0755
notify: restart_grafana
grafana_admin_user: "admin" grafana_admin_password: "password"
phase2
role monito
prometheus.yml.j2
#jinja2: lstrip_blocks: "True"
{{ prometheus_var_config | to_nice_yaml(indent=2) }}
{% if prometheus_node_exporter_group %}
- job_name: node_exporter
scrape_interval: 15s
static_configs:
- targets:
{% for server in groups[prometheus_node_exporter_group] %}
- {{ server }}:9100
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
prometheus.j2
# Set the command-line arguments to pass to the server.
ARGS="--web.enable-lifecycle --storage.tsdb.retention.time={{ prometheus_retention_time }} --web.console.templates=/etc/prometheus/consoles --web.console.libraries=/etc/prometheus/console_libraries
---
# handlers file for roles/monito
- name: restart_prometheus
systemd:
name: prometheus
state: restarted
enabled: yes
daemon_reload: yes
- name: reload_prometheus
uri:
url: http://localhost:9090/-/reload
method: POST
status_code: 200
---
# tasks file for roles/monito
- name: update and install prometheus
apt:
name: prometheus
state: latest
update_cache: yes
cache_valid_time: 3600
- name: prometheus args
template:
src: prometheus.j2
dest: /etc/default/prometheus
mode: 0644
owner: root
group: root
notify: restart_prometheus
- name: prometheus configuration file
template:
src: prometheus.yml.j2
dest: "{{ prometheus_dir_configuration }}/prometheus.yml"
mode: 0755
owner: prometheus
group: prometheus
notify: reload_prometheus
- name: start prometheus
systemd:
name: prometheus
state: started
enabled: yes
- meta: flush_handlers
---
# defaults file for roles/monito
prometheus_dir_configuration: "/etc/prometheus"
prometheus_retention_time: "365d"
prometheus_scrape_interval: "30s"
prometheus_node_exporter: true
prometheus_node_exporter_group: "all"
prometheus_env: "production"
prometheus_var_config:
global:
scrape_interval: "{{ prometheus_scrape_interval }}"
evaluation_interval: 5s
external_labels:
env: '{{ prometheus_env }}'
scrape_configs:
- job_name: prometheus
scrape_interval: 5m
static_configs:
- targets: ['{{ inventory_hostname }}:9090']
phase1
LES TASKS DU ROLE
* vérifier si node exporter est déjà installé
roles node-exporter
node_exporter.service.j2
[Unit]
Description=Node Exporter Version {{node_exporter_version}}
After=network-online.target
Wants=network-online.target
[Service]
User={{ node_exporter_user }}
Group={{ node_exporter_user }}
Type=simple
ExecStart={{ node_exporter_bin }}
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
handler
---
# handlers file for roles/node-exporter
- name: reload_daemon_and_restart_node_exporter
systemd:
name: node_exporter
state: restarted
daemon_reload: yes
enabled: yes
tasks
---
# tasks file for roles/node-exporter
- name: check if node exporter exist
stat:
path: "{{ node_exporter_bin }}"
register: __check_node_exporter_present
- name: create node exporter user
user:
name: "{{ node_exporter_user }}"
append: true
shell: /usr/sbin/nologin
system: true
create_home: false
home: /
- name: create node exporter config dir
file:
path: "{{ node_exporter_dir_conf }}"
state: directory
owner: "{{ node_exporter_user }}"
group: "{{ node_exporter_group }}"
# on récupère la version via le module shell
- name: if node exporter exist get version
shell: "cat /etc/systemd/system/node_exporter.service | grep Version | sed s/'.*Version '//g"
when: __check_node_exporter_present.stat.exists == true
changed_when: false
register: __get_node_exporter_version
- name: download and unzip node exporter if not exist
unarchive:
#src: "https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter/releases/download/v{{ node_exporter_version }}/node_exporter-{{ node_exporter_version }}.linux-amd64.tar.gz"
src: "https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter/releases/download/v{{ node_exporter_version }}/node_exporter-{{ node_exporter_version }}.{{ node_exporter_platform }}.tar.gz"
dest: /tmp/
remote_src: yes
# when: __check_node_exporter_present.stat.exists == false
when: __check_node_exporter_present.stat.exists == false or not __get_node_exporter_version.stdout == node_exporter_version
- name: move the binary to the final destination
copy:
src: "/tmp/node_exporter-{{ node_exporter_version }}.{{ node_exporter_platform}}/node_exporter"
dest: "{{ node_exporter_bin }}"
owner: "{{ node_exporter_user }}"
group: "{{ node_exporter_group }}"
mode: 0755
remote_src: yes
# when: __check_node_exporter_present.stat.exists == false
when: __check_node_exporter_present.stat.exists == false or not __get_node_exporter_version.stdout == node_exporter_version
- name: clean
file:
path: "/tmp/node_exporter-{{ node_exporter_version }}.{{ node_exporter_platform}}/node_exporter"
state: absent
- name: install service
template:
src: node_exporter.service.j2
dest: /etc/systemd/system/node_exporter.service
owner: root
group: root
mode: 0755
notify: reload_daemon_and_restart_node_exporter
- meta: flush_handlers
- name: service always started
systemd:
name: node_exporter
state: started
enabled: yes
default
---
# defaults file for roles/node-exporter
node_exporter_version: "1.0.1"
node_exporter_bin: /usr/local/bin/node_exporter
node_exporter_user: node-exporter
node_exporter_group: "{{ node_exporter_user }}"
node_exporter_dir_conf: /etc/node_exporter
node_exporter_platform: "linux-arm64"
3 roles
nginx
- name: install nginx apt: name: nginx,curl state: present cache_valid_time: 3600 update_cache: yes - name: remove default file file: path: "{{ item }}" state: absent with_items: - "/etc/nginx/sites-available/default" - "/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default" - name: install vhost template: src: default_vhost.conf.j2 dest: /etc/nginx/sites-available/default_vhost.conf owner: root group: root mode: 0644 notify: reload_nginx - name: Flush handlers meta: flush_handlers users
- name: création du user devops user: name: devops shell: /bin/bash groups: sudo append: yes password: "{{ 'password' | password_hash('sha512') }}" become: yes - name: Add devops user to the sudoers copy: dest: "/etc/sudoers.d/devops" content: "devops ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL" become: yes - name: Deploy SSH Key authorized_key: user: devops key: "{{ lookup('file', '/tmp/xavki.pub') }}" state: present become: yes
ssh_keygen
- name: mon premier playbook hosts: localhost connection: local roles: - ssh_keygen - name: generate SSH key" openssh_keypair: path: /tmp/xavki type: rsa size: 4096 state: present force: no
creer: un dossier roles executer: ansible-galaxy init monrole résultat: tree -a . └── monrole ├── defaults │ └── main.yml ├── files ├── handlers │ └── main.yml ├── meta │ └── main.yml ├── README.md ├── tasks │ └── main.yml ├── templates ├── tests │ ├── inventory │ └── test.yml ├── .travis.yml └── vars └── main.yml
Documentation :
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/user_guide/playbooks_environment.html
Objectifs : Définir des variables d'environnement et utiliser un prompt
* différents endroits pour définir les variables d'environnement
* playbook
* tasks
prompt
* var prompt : interrogation de l'utilisateur
vars_prompt:
- name: nom
tasks:
- name: echo
shell: "echo Salut {{ nom }}"
register: __output
- name: print
debug:
var: __output
* avec phrase et valeur par défaut
vars_prompt:
- name: env
prompt: "Quel est votre environnement ? prod/stage/dev"
default: dev
environment:
ENV: "{{ env }}"
tasks:
- name: echo
shell: "echo Salut $ENV"
register: __output
- name: print
debug:
var: __output
* exemples:
- name: utilisation du module shell et command
hosts: all
environment:
PATHLIB: "/var/lib/"
ENV: "{{ env }}"
vars_prompt:
- name: nom
- name: env
prompt: "Quel est votre environnement ? prod/stage/dev"
default: dev
tasks:
- name: echo
shell: echo $PATHLIB
register: __output
changed_when: false
- name: print
debug:
var: __output
- name: echo
shell: "echo Salut $ENV"
register: __output
- name: print
debug:
var: __output
environment
- name: utilisation du module shell et command
hosts: all
environment:
PATHLIB: "/var/lib/"
tasks:
- name: echo
shell: echo $PATHLIB
register: __output
- name: print
debug:
var: __output
* variable d'environnement de la machine ansible
- name: echo
shell: "echo {{ lookup('env', 'ENV') | default('stage', True) }}"
register: __output
- name: print
debug:
var: __output
docker
* Objectif : construction, build et push d'images docker
Documentation :
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/collections/community/general/docker_image_module.html
Prérequis :
* docker * python3-docker ou pip3 install docker
PARAMETRES :
* api_version : version de l'api docker (docker info)
* archive_path : cas d'une image en tar, chemin d'accès
* build : pour constuire une image * args : clef/valeur * cache_from : images sources utilisées en cache * container_limits: limite applicable aux conteneurs POUR LE BUILD * cpusetcpus : spécificier le cpu (taskset) * cpushares : poids des cpus * memory : mémoire maximum * memswap : mémoire total (mem + swap) , -1 = disable swap
* dockerfile : nom du fichier Dockerfile * /etc/hosts : utilisé lors du build (liste : ip / adresses) * http_timeout : timeout lors du build * network : utilisé pour le RUN * no_cache: ne pas utiliser de cache * path : chemin de contexte pour le build * pull : dowload du/des FROM * rm : suppression des images intermédiaires après le build * target : image finale résultant de plusieurs stage * use_config_proxy : utilisation d'un proxy
* buildargs (deprecated) : idem build > args
* ca_cert : vérficiation du serveur par ca (DOCKER_CERT_PATH)
* client_cert : tls client
* client_key : tls client clef
* containers_limit (deprecated) : idem build > container_limits
* debug : activation du mode debug
* docker_hosts : par défaut socket local sinon tcp/ssh
* dockerfile (deprecated) : cf build
* force : à utiliser avec le state absent pour forcer la suppression
* force_source : refaire build, load, pull d'une image qui existe déjà
* force_tag : forcer le tagging d'une image
* load_path : load une image via son archive tar
* name : nom de l'image url_registry/nom
* nocache : ne pas utiliser le cache au build
* path (deprecated) : cf build
* pull : idem
* push : idem
* repository : chemin vers le dépôt
* rm (deprecated) : cd build
* ssl_version : version ssl pour docker
* state : present / build / absent
* tag : tag de l'image
* timeout : délai pour le timeout du daemon docker
* tls : connexion chiffrée vers l'api docker
* tls_hostname : hostname pour le tls
* validate_certs : check tls
login
* cas du build & push
- include_vars: /home/oki/.vault.yml
- name: docker login
docker_login:
registry_url: registry.gitlab.com
username: xavki
password: "{{ vault_token_gitlab }}"
reauthorize: yes
- name: build
docker_image:
build:
path: /tmp/build/
dockerfile: Dockerfile
pull: yes
cache_from:
- alpine:3.9
source: build
name: registry.gitlab.com/xavki/testflux
tag: v1.1
Container
* Objectif : lancement d'image docker
Documentation :
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/collections/community/general/docker_container_module.html
Prérequis :
* docker * python3-docker ou pip3 install docker
PARAMETRES :
image
* pull simple d'une image
- name: Pull an image
docker_image:
name: alpine
tag: latest
source: pull
* retaguer une image
- name: Pull an image
docker_image:
name: alpine
tag: latest
repository: myregistry/monimage:v1.0
* import via un tar (docker save)
- name: copy image
copy:
src: image.test.v1.0.tar
dest: /tmp/
- name: Pull an image
docker_image:
name: archive
tag: v1.0
load_path: /tmp/image.test.v1.0.tar
source: load
Exemple build
* build d'image via Dockerfile
- name: copy files
file:
path: /tmp/build
state: directory
- name: copy image
copy:
src: app/
dest: /tmp/build
- name: build
docker_image:
name: imgbuild
tag: v1.0
source: build
build:
path: /tmp/build/app/
dockerfile: Dockerfile
cache_from:
- alpine:3.9
* cas du build & push
- include_vars: /home/oki/.vault.yml
- name: docker login
docker_login:
registry_url: registry.gitlab.com
username: xavki
password: "{{ vault_token_gitlab }}"
reauthorize: yes
- name: build
docker_image:
build:
path: /tmp/build/
dockerfile: Dockerfile
pull: yes
cache_from:
- alpine:3.9
source: build
name: registry.gitlab.com/xavki/testflux
tag: v1.2
push: yes
assemble
Documentation :
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/collections/ansible/builtin/assemble_module.html
PARAMETRES
* backup : sauvegarde du fichier avant changement
* decrypt : déchiffrer automatiquement par défaut ou pas le vault
* delimiter : séparation entre chaque fichier
* dest : la destination (fichier)
* group : groupe du fichier de destination
* regexp : regular expression de pattern des fichiers sources
* remote_src
* src : répertoire source
* simple via uniquement le remote
- name: dir
file:
path: /tmp/sources
state: directory
- name: copy
copy:
src: "files/{{ item }}"
dest: /tmp/sources/
with_items:
- t1
- t2
- t3
- name: test assemble
assemble:
src: /tmp/sources
dest: /tmp/myconf.cfg
* ajouter un delimiter
delimiter: '### START FRAGMENT ###'
* sans remote src
- name: test assemble
assemble:
src: files/
dest: /tmp/myconf.cfg
remote_src: no
Shell/command
Documentation :
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/2.5/modules/shell_module.html
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/collections/ansible/builtin/command_module.html
Objectifs : lancer des commandes shell
Command vs Shell > command : options réduites (lance des commandes simples) shell : utilisation de tout ce qui est dans la CLI (pipe...)
PARAMETRES : COMMAND
* argv : ligne de commande sous forme de liste
* chdir : change de répertoire
* cmd : commande lancée
* creates : la commande n'est pas lancée si le fichier existe
* removes : inverse de creates, si le fichier existe la commande est lancée
* stdin : spécifier une valeur entrante via stdin
* stdin_add_newline : passe une ligne pour le stdin
* strip_empyt_ends : supprimer les lignes vides
* simple :
- name: test
command:
cmd: ls
register: __output
* changement de directory :
- name: test
command:
cmd: ls
chdir: /etc/
register: __output
ANSIBLE : Modules COMMAND & SHELL
* commande en liste :
- name: test
command:
argv:
- ls
- -larth
register: __output
* sous condition si le fichier n'existe pas
- name: touch
file:
path: /tmp/xavki
state: touch
- name: test
command:
cmd: ls -lath /tmp
creates: /tmp/xavki
register: __output
- name: debug
debug:
var: __output
ANSIBLE : Modules COMMAND & SHELL
* inverse : si il existe
- name: test
command:
cmd: ls -lath /tmp
removes: /tmp/xavki
ANSIBLE : Modules COMMAND & SHELL
PARAMTRES : SHELL
* chdir : changement de répertoire d'exécution
* creates : la commande est lancée si le fichier n'existe pas
* executable : choix du shell utilisé
* removes : inverse de creates
* stdin : définir un stdin
* warn : afficher ou non les warn
ANSIBLE : Modules COMMAND & SHELL
* exemple simple :
- name: test
shell: cat /etc/hosts | grep 127
register: __output
- name: debug
debug:
var: __output
* exemple avec un bloc
- name: test
shell: |
cat /etc/hosts
ls /etc/
register: __output
- name: debug
debug:
var: __output
* exemple avec des variables d'environnement
- name: test
shell: echo "Hello $MAVAR"
environment:
MAVAR: "xavki"
register: __output
uri
Objectifs : passer des requêtes http ou https et interagir avec
PARAMETRES :
* HEADER_ : paramètre header pour passer vos requêtes
* body : si activation du format json récupérer une variable
* body_format : format du body json ou raw
* creates : si le fichier existe la tâche n'est pas lancée
* dest : répertoire de destination
* follow_redirects : suivre les redirections
* force_basic_aut : forcer le basic auth
* headers : ajout de header (format yaml)
* method : GET / POST/ DELETE / PUT / HEAD / PATCH / TRACE...
* others : autre argument pour le file module (fichier créé)
* password : pour le basic auth
* removes : supprime le fichier avant
* return_content : pour récupérer le contenu
* status_code : 200, 301... [200,201...]
* timeout : en seconde
* url : target
* user : pour basic_auth
* validate_certs : stricte tls ou non
* cas simple
- name: test
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: uri
uri:
url: http://xavki.blog
method: GET
validate_certs: False
* vérification du status
- name: test
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: uri
uri:
url: http://xavki.blog
method: GET
validate_certs: False
status_code: 200
ANSIBLE : Module URI
* liste de code retour
- name: uri
uri:
url: https://httpbin.org/status/500
method: POST
status_code: [200,201,301]
validate_certs: False
* récupération du contenu
- name: test
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: uri
uri:
url: http://httpbin.org/get
return_content: yes
method: GET
register: __content
- name: debug
debug:
var: __content.content
ANSIBLE : Module URI
* utilisation du format json
- name: uri
uri:
url: https://httpbin.org/get
method: GET
return_content: yes
validate_certs: False
body_format: json
register: __body
- name: debug
debug:
var: __body.json.url
* validation du contenu
- name: test
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: uri
uri:
url: http://xavki.blog
return_content: yes
method: GET
validate_certs: False
register: __content
failed_when: " 'xavki' not in __content.content"
ANSIBLE : Module URI
* basic auth
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: uri
uri:
url: https://httpbin.org/basic-auth/toto/test
user: "toto"
password: "test"
method: GET
validate_certs: False
- name: uri2
uri:
url: https://httpbin.org/basic-auth/tot/test
user: "toto"
password: "test"
method: GET
validate_certs: False
Gather Facts & module Setup
Documentation : * setup : https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/2.3/setup_module.html * gather facts : https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/user_guide/playbooks_vars_facts.html
* facts > données relatives aux machines plus ou moins détaillées (réduit, non collectés...) * networks * devices * os * hardware * connexion utilisée * montages/volumes...
* ansible_facts : dictionnaire contenant tous les facts
set_fact
Documentation :
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/collections/ansible/builtin/set_fact_module.html
PARAMETRES
* cacheable : ajouté au cache (défaut non)
- name: set fact
set_fact:
mavariable: "Hello tout le monde !!"
- name: debug
debug:
var: mavariable
* exemple avec éléments calculés
vars:
var1: "hello"
var2: "je suis"
tasks:
- name: get user
command: "echo $USER"
register: __user
- name: date
set_fact:
mavariable: "{{ var1 }} {{ var2 }} {{ __user.stdout }} sur {{ ansible_hostname }}"
- name: debug
debug:
var: mavariable
* le gather fact datetime :
- name: date
debug:
var: ansible_date_time
* si cache (ansible.cfg)
#cache facts gathering = smart fact_caching = jsonfile fact_caching_connection = /tmp/facts_cache # two hours timeout fact_caching_timeout = 7200
* contourner le cache
- name: date without cache
shell: "date +%Y-%m-%d"
register: shell_date
- set_fact:
date: "{{ shell_date.stdout }}"
ansible-playbook -i 00_inventory.yml -D pbfact.yml
PLAY [exemple synchro] ********************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ********************************************************************************
ok: [172.17.0.5]
ok: [172.17.0.3]
ok: [172.17.0.4]
ok: [172.17.0.2]
TASK [get user] ***************************************************************************************
changed: [172.17.0.2]
changed: [172.17.0.4]
changed: [172.17.0.3]
changed: [172.17.0.5]
TASK [date] *******************************************************************************************
ok: [172.17.0.3]
ok: [172.17.0.4]
ok: [172.17.0.5]
ok: [172.17.0.2]
TASK [debug] ******************************************************************************************
ok: [172.17.0.5] => {
"mavariable": "hello je suis samik sur samik-debian-4"
}
ok: [172.17.0.3] => {
"mavariable": "hello je suis samik sur samik-debian-2"
}
ok: [172.17.0.4] => {
"mavariable": "hello je suis samik sur samik-debian-3"
}
ok: [172.17.0.2] => {
"mavariable": "hello je suis samik sur samik-debian-1"
}
PLAY RECAP ********************************************************************************************
172.17.0.2 : ok=4 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
172.17.0.3 : ok=4 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
172.17.0.4 : ok=4 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
172.17.0.5 : ok=4 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
* soit en cli
ansible -i 00_inventory.yml all -m setupansible -i 00_inventory.yml all -m setup -a "filter=ansible_user*" - name: debug debug: var: ansible_factsapt_key
PARAMETRES :
* data > directement fournir la clef
file : chemin vers un fichier contenant la clef
id : identifiant de la clef (pour la supprimer)
keyring : le chemin vers la clef en place
keyserver : le serveur où trouver la clef
state : present/absent
url : url pour télécharger la clef
validate_certs : valider strictement ou non le certificat
Exemple avec docker
Quelques exemples :
* à partir d'un fichier
- name: Add a key from a file on the Ansible server. apt_key: data: "{{ lookup('file', 'apt.asc') }}" state: present- name: Add an Apt signing key to a specific keyring file apt_key: id: 9FED2BCBDCD29CDF762678CBAED4B06F473041FA url: https://ftp-master.debian.org/keys/archive-key-6.0.asc keyring: /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/debian.gpg- name: Remove a Apt specific signing key, leading 0x is valid apt_key: id: 0x9FED2BCBDCD29CDF762678CBAED4B06F473041FA state: absentlinefile
exemples 2
avec regexp sous condition:
- name: change admin user
lineinfile:
path: /etc/grafana/grafana.ini
regexp: "{{ item.before }}"
line: "{{ item.after }}"
with_items:
- { before: "^;admin_user = admin", after: "admin_user = {{ grafana_admin_user }}"}
- { before: "^;admin_password = admin", after: "admin_password = {{ grafana_admin_password }}"}
* cas le plus simple mais le moins courant : ajout d'une ligne
```
- name: lineinfile
lineinfile:
dest: /tmp/test.conf
line: "test"
state: present
create: True
```
Rq: si changement de line > nlle ligne
* recherche d'une ligne précise et modification
```
lineinfile:
dest: /tmp/test.conf
line: "test 2"
regexp: "^test$"
state: present
create: True
```
<br>
* modification avec capture
```
lineinfile:
dest: /tmp/test.conf
line: 'je suis le nombre : \1'
regexp: "^test ([0-2])$"
backrefs: yes
state: present
create: True
```
Rq: si 2 runs attention
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# ANSIBLE : Modules LINEINFILE
<br>
* commenter une ligne avec plus ou moins de précision
```
lineinfile:
dest: /tmp/test.conf
line: '# \1'
regexp: "(^je suis le nombre : [0-2])"
backrefs: yes
state: present
create: True
```
<br>
* ajout avant une ligne
```
lineinfile:
dest: /tmp/test.conf
line: "Ma nouvelle ligne"
insertbefore: '# je suis le nombre : [0-2]'
state: present
create: True
```
Rq : idem after
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# ANSIBLE : Modules LINEINFILE
<br>
* supprimer une ligne soit par regexp ou par line
```
- name: lineinfile
lineinfile:
dest: /tmp/test.conf
regexp: "^Ma nouvelle ligne"
#line: "^Ma nouvelle ligne"
state: absent
```
<br>
* avec backup avant modification
```
- name: lineinfile
lineinfile:
dest: /tmp/test.conf
regexp: "^#"
state: absent
backup: yes
```
get-url
Documentation : * https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/collections/ansible/builtin/get_url_module.html
PARAMETRES :
* attributes
backup : garde un backup du fichier avant (horodaté)
checksum : vérifie le fichier à l'arrivée
client_cert : pour la certification cliente tls
client_key : non nécessaire pour tls
dest : chemin où le fichier est stocké
force : remplacement du fichier existant ou pas (si destination est un fichier)
force_basic_auth : pour utiliser l'identification basic auth
group : groupe propriétaire
headers : ajouter un header personnalisé à la requête
* http_agent: spécifier un agent
mode : permissions (0755 ou u+rwx,g+rx,o+rx)
owner : propriétaire du fichier
sha256sum : calcul du sha256 après téléchargement
timeout : limite la durée de la requête
tmp_dest : localisation temporaire pour le téléchargement
unsafe_writes : ne pas éviter la corruption de fichier
url : url de la source (http/https, ftp)
url_password : pour le basic_auth
url_username : pour le basic_auth
use_proxy : si derrière un proxy
validate_certs : validation du certificats
Exemple27
- name: dest locale puis dispatch
get_url:
url: https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter/releases/download/v1.0.1/node_exporter-1.0.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
dest: /tmp/
validate_certs: no
delegate_to: localhost
run_once: yes
- name: dispatch
unarchive:
src: /tmp/node_exporter-1.0.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
dest: /tmp/
archive
Documentation :* https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/2.5/modules/unarchive_module.html
Prérequis : unzip, tar
PARAMETRES :
* attributes : attributs du fichier
* copy : deprecated > utiliser remote_src
* creates : si un répertoire ou fichier exist la tâche n'est pas lancé
* decrypt : (default yes) déchiffrer les fichiers vaultés
* dest : destination des éléments
* exclude : fichier ou chemin à exclure de unarchive
* extra_opt : options complémentaires
* group : groupe propriétaire
* keep_newer : garder le plus récent
* list_files : retourne la liste des fichiers de l'archive
* mode : permissions (0755, u+rwx,g+rx,o+rx)
* remote_src : passer par le host ansible pour pousser récupérer l'archive
* src : no > copy du fichier vers les cibles, yes > download et pousse
* unsafe_writes : éviter les corruptions de fichiers
* validate_certs : dans le cas de https (default yes)
Exemple26
* copy de la machine ansible et dezip sur la machine cible:
- name: test unarchive unarchive: src: /tmp/node_exporter-1.0.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz dest: /home/oki/
* avec url utilisation de remote_src
- name: test unarchive unarchive: src: https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter/releases/download/v1.0.1/node_exporter-1.0.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz dest: /home/oki/ remote_src: yes
- name: unarchive /get url
hosts: all
become: yes
tasks:
- name: installation de tar unzip
apt:
name: "{{ pkg}}"
update_cache: yes
state: present
cache_valid_time: 3600
vars:
pkg:
- tar
- unzip
- name: test unarchive local
unarchive:
src: /tmp/zip.tgz
dest: /home/samik/
- name: test unarchive via https
unarchive:
src: https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter/releases/download/v1.0.1/node_exporter-1.0.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
dest: /home/samik/
remote_src: yes
- name: dest locale puis dispatch
get_url:
url: https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter/releases/download/v1.0.1/node_exporter-1.0.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
dest: /tmp/
validate_certs: no
delegate_to: localhost
run_once: yes
- name: dispatch
unarchive:
src: /tmp/node_exporter-1.0.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
dest: /tmp/
autre fichier:
- name: test unarchive/geturl
hosts: all
become: yes
tasks:
- name: test unarchive
unarchive:
src: /tmp/node_exporter-1.0.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
dest: /home/samik/
- name: test unarchive
unarchive:
src: https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter/releases/download/v1.0.1/node_exporter-1.0.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
dest: /home/samik/
remote_src: yes
- name: start haproxy service
get_url:
url: https://downloads.apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-10/v10.0.0-M9/bin/apache-tomcat-10.0.0-M9.tar.gz
dest: /opt/tomcat8.tar.gz
mode: 0755
checksum: sha512:547ae280792b8684d11154f678584d0c4eb5af645cc8145e04da6de6d115b7bca03122191e6447cdb3497b85357181ca3fd9716d8a2dbc86461cf28f3df3ee91
group: samik
owner: samik
systemd
Documentation :
Objectifs : gestion des services systemd et reload
Documentation : https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/2.5/modules/systemd_module.html
PARAMETRES :
* daemon_reexec :
* daemon_reload : exécute un reload pour prendre en compte les changements de conf systemd
* enabled : active le démarrage au boot du service
* force : écraser les liens symboliques systemd
* masked : masquer l'unité systemd
* name : nom du service systemd
* no_block : ne pas attendre la fin de l'opération pour continuer
* scope: systemd manager pour un user ou l'ensemble des users
* state : started /stopped / reloaded / restarted
* user : deprecated
Exemple25
* le plus simple :
- name: Make sure a service is running systemd: name: haproxy state: started- name: Make sure a service is running systemd: name: haproxy state: started- name: Make sure a service is running systemd: name: haproxy state: started enabled: yes- name: Make sure a service is running systemd: name: haproxy state: started enabled: yes daemon-reload: yes- name: Make sure a service is running systemd: name: haproxy state: started enabled: yes daemon-reload: yes masked: no- name: Make sure a service is running systemd: daemon-reload: yeshandlers
flush des handlers
* attention quand jouer le trigger ? par defaut, il est joué toujours en fin de playbook, le flush permet de resetter en cours de PB.
- name: Flush handlers meta: flush_handlers- name: Check if need to restart stat: path: /var/run/reboot.pending register: __need_reboot changed_when: __need_reboot.stat.exists notify: reboot_serverexemple24
template
exemple au début du fichier
#{{ template_run_date }} - "{{ ansible_managed }}" via {{ template_uid }}@{{ template_host }}Sortie
Fetch
permet de récupérer un fichier sur hote distant, ici test avec /etc/host
PB
Exemple22
Exemples avec nginx
COPY
PARAMETRES :
* attributes : attributs du fichier
* backup : réalise une copie datée avant la copie
* checksum : vérification du ficheir via un hash
* content : dans le cas ou la source n'est pas un fichier mais une variable ou un string
* decrypt : déchiffre les fichiers si ils sont vaultés (défaut : yes)
* dest : localisation du fichier sur les serveurs target
* dicrectory_mode : dans le cas d'une recopie en mode récursif
* follow : indiquer le filesytème dans la destination
* force : remplace le fichier si il est différent de la source
* group : group propriétaire
* local_follow : indique le FS dans la source
* mode : permissions du fichier ou du répertoire (0755, u+rwx,g+rx,o+rx)
* owner : user propriétiare
* remote_src : no > copie du master vers la target, yes > copie de la target vers la target
* src : localisation de la source* attention : roles / dir files / .
* unsafe_writes : éviter la corruption de fichier
validate : commande jouée pour valider le fichier avant de le copier (le fichier se situe %s)
Exemple20
Exemple21
Exemple17
Exemple18
Exemple19
* combinaison avec with_items
vars: mesfichiers: - { source: "xavki1.txt", destination: "/tmp/{{ ansible_hostname }}_xavki1.txt", permission: "0755" } - { source: "xavki2.txt", destination: "/home/oki/{{ ansible_hostname }}_xavki2.txt", permission: "0644" } tasks: - name: copy copy: src: "{{ item.source }}" dest: "{{ item.destination }}" mode: "{{ item.permission }}" with_items: "{{ mesfichiers }}" Delegate, run_once, local
Exemple16
Objectifs : gérer les run locaux ou déléguer des tâches* primaire/secondaire
* delegate_to : déléguer une tache à un autre serveur identifié
- name: premier playbook hosts: all tasks: - name: création de fichier file: state: touch path: /tmp/xavki.txt delegate_to: localhostRq : attention au nombre d'itération si plusieurs serveurs
* quelles variables ?
- name: premier playbook hosts: all tasks: - name: debug debug: var: var1 - name: debug debug: var: var1 delegate_to: localhostssh
Rq : si password / clef cassé > force : yes
exemple15
Reboot
l'inventory:
exemple14
exemple13
yum
exemple3
exemple12
with_items
Conditionner les taches d'Ansible
Exemple11
Exemple10
vars: fichiers: - { dir: "xavki1", file: "fichierA"} - { dir: "xavki2", file: "fichierB"} - { dir: "xavki3", file: "fichierC"} - { dir: "xavki4", file: "fichierD"} tasks: - name: création de fichiers file: path: /tmp/xavki/{{ item.dir }}/{{ item.file }} state: touch with_items: - "{{ fichiers }}" with_items: - "{{ groups['all'] }}" - name: création de fichiers file: path: /tmp/{{ item }} state: touch with_inventory_hostnames: - allexemple9
register & stat
exemple7
* récupération d'une clef
- name: debug debug: var: __fichier_xavki.stat.exists - name: création répertoire xavki file: path: /tmp/xavki state: directory when: __fichier_xavki.stat.exists tasks: - name: création d'un fichier file: path: /tmp/xavki.txt state: touch owner: root when: xavki_file is defined - name: check avec stat stat: path: /tmp/xavki.txt register: __fichier_xavki - name: debug debug: var: __fichier_xavki.stat.exists - name: création répertoire xavki file: path: /tmp/xavki state: directory when: __fichier_xavki.stat.exists and xavki_file is definedexemple8
playbook
sortie
exemple6
* création d'un fichier
- name: création d'un fichier file: path: /tmp/xavki.txt state: touch owner: xavki - name: check avec stat stat: path: /tmp/xavki.txt - name: check avec stat stat: path: /tmp/xavki.txt register: __fichier_xavki_exist - name: debug debug: var: __fichier_xavkiuser
exemple5
examples4
* création d'un user avec password
- name: création de xavki user: name: xavki state: present password: "{{ 'password' | password_hash('sha512') }}" - name: création de xavki user: name: xavki state: present groups: sudo append: yes password: "{{ 'password' | password_hash('sha512') }}" file
exemple3:
* touch avec idempotence
- name: touch idempotent file: path: /tmp/xavki.txt state: touch mode: 0755 modification_time: preserve access_time: preserve - name: touch sans idempotence file: path: /tmp/xavki/1/2/3 state: touch mode: 0755 modification_time: now access_time: nowexemple2: file
* modification du groupe et des droits (RWX-RX-RX - 0755) | stat
- name: création du répertoire /tmp/xavki file: path: /tmp/xavki/ state: directory owner: root group: root mode: 0755 become: yes - name: création du répertoire /tmp/xavki file: path: /tmp/xavki/1/2/3/4 recurse: yes state: directory owner: root group: root mode: 0755 - name: création du répertoire /tmp/xavki file: path: /tmp/xavki/1/2/3/4/fichier.txt state: touch owner: root group: root mode: 0755suite...
* lien symbolique = lien vers fichier (diff avec hardlink = lien vers inode)
- name: création du répertoire /tmp/xavki file: src: /tmp/xavki/1/2/3/4/ dest: /tmp/symlink state: link #hard owner: root group: root mode: 0755Rq: idempotence
* suppression de fichier
- name: dir sans idempotence file: path: /tmp/xavki.txt state: absent - name: dir sans idempotence file: path: /tmp/xavki/ state: absent
-name: titre de l'action
hosts: all
-become: yes
tasks:
exemples
- name: Mon Playbook !! hosts: all remote_user: vagrant become_user: yes tasks: - name: je debug debug: msg: "{{ var1 }}" ansible all -m gather_facts --tree /tmp/facts
exemple
ansible -i "node2," all -m gather_facts -a "filter=ansible_distribution*"
récupérer un fichier
ansible -i "node2," all -m fetch -a 'src=/tmp/titi.txt dest=xavki.txt flat=yes'
flat = fichier plat
idem scp
ansible -i "node2," all -m copy -a 'src=toto.txt dest=/tmp/titi.txt'
ansible -i "node2," all -b -m service -a 'name=nginx state=stopped'
ansible -i "node2," all -b -m apt -a 'name=nginx state=latest'
ansible -i 00_inventory.yml centos -b -m raw -a "yum install python38 -y "
ansible -i "node2," all -u vagrant -b -K -m raw -a "apt install -y git"
ansible all -b -e "var1=xavki" -m debug -a 'msg={{ var1 }}'
ansible -i "node2," all -u vagrant -m shell -a "ps aux | grep vagrant | wc -l" --one-line
detail:
-m = module shell -a = argument "ps aux | grep vagrant | wc -l" --one-line = sortie sur une ligne ansible -i "node2," all -u vagrant -m command -a uptime
imackris | UNREACHABLE! => {
"changed": false,
"msg": "Failed to connect to the host via ssh: ssh: Could not resolve hostname imackris: nodename nor servname provided, or not known",
"unreachable": true
}
[WARNING]: Platform linux on host abacus is using the discovered Python interpreter at /usr/bin/python,
but future installation of another Python interpreter could change this. See
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/2.9/reference_appendices/interpreter_discovery.html for more
information.
abacus | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
[WARNING]: Platform linux on host kaisenlinux is using the discovered Python interpreter at
/usr/bin/python, but future installation of another Python interpreter could change this. See
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/2.9/reference_appendices/interpreter_discovery.html for more
information.
kaisenlinux | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
[WARNING]: Platform darwin on host imacpat is using the discovered Python interpreter at
/usr/bin/python, but future installation of another Python interpreter could change this. See
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/2.9/reference_appendices/interpreter_discovery.html for more
information.
imacpat | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
mbp | UNREACHABLE! => {
"changed": false,
"msg": "Failed to connect to the host via ssh: ssh: connect to host mbp port 22: Operation timed out",
"unreachable": true
}
nexus | UNREACHABLE! => {
"changed": false,
"msg": "Failed to connect to the host via ssh: ssh: connect to host nexus port 2222: Operation timed out",
"unreachable": true
}
ipadkris | UNREACHABLE! => {
"changed": false,
"msg": "Failed to connect to the host via ssh: ssh: connect to host ipadkris port 22: Operation timed out",
"unreachable": true
}
ansible all -i "localhost," -m debug -a "msg='Hello Ansible'"
-i
inventory
fichier inventaire
plusieurs lieux possible, défini par ordre de priorité
inventory = /etc/ansible/hostsforks = 5sudo_user = rootask_sudo_pass = Trueask_pass = Truegathering = implicitgather_subset = allroles_path = /etc/ansible/roleslog_path = /var/log/ansible.logvault_password_file = /path/to/vault_password_filefact_caching_connection =/tmppipelining = Falseview
depend de l'emplacement
astuce pour localiser le fichier config pris en compte:
list
.ansible
ll -R $HOME/.ansible*
-rw-r--r-- 1 samik staff 19K 3 mai 11:31 /Users/samik/.ansible.cfg
/Users/samik/.ansible:
total 0
drwx------ 2 samik staff 64B 12 aoû 18:30 cp
drwx------ 2 samik staff 64B 12 aoû 18:29 tmp
/Users/samik/.ansible/cp:
.ansible.cfg