Valentina Becerra Álvarez
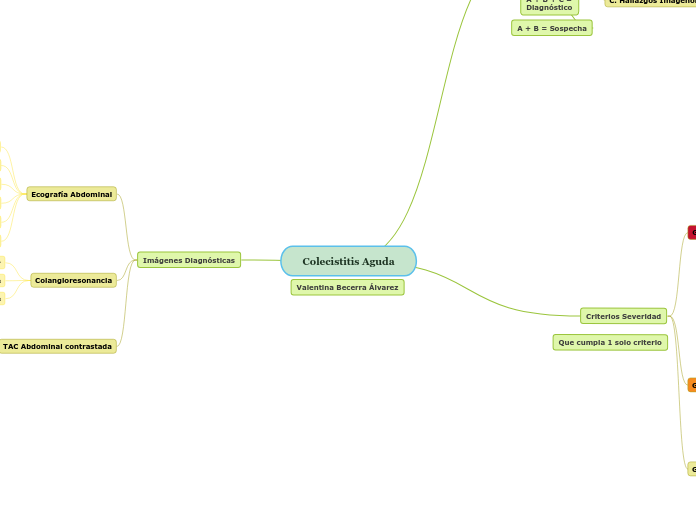
Que cumpla 1 solo criterio
A + B + C = Diagnóstico
A + B = Sospecha
Colecistitis Aguda
Tenses demonstrate the time of actions centered around the subject of the sentence. These actions are called verbs and change according to tenses.
Imágenes Diagnósticas
There are four Future tenses:
- Future Simple ('with Will' and 'with Going to')
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
TAC Abdominal contrastada
Future Perfect Simple is used for:
- an action that will be finished by a particular time in the future
- an action that starts before and continues up to another action or time in the future
- an action that will finish before a certain time in the future, but it is not known exactly when
Adverb used with Future Continuous:
- tomorrow (e.g. tomorrow by 7)
Áreas de alta densidad grasa perivesicular
Distensión vesicular
Structure:
Will + Subject + Have + Past Participle?
e.g. Will you have met your colleague by this time tomorrow?
Colecciones perivesiculares
Structure:
Subject + Won’t Have + Past Participle
e.g. I won’t have met my friend form United States by this time tomorrow.
Engrosamiento pared vesicular
Structure:
Subject + Will Have + Past Participle
e.g. I will have met my friend form United States by this time tomorrow.
Colangioresonancia
Future Continuous is used:
- for an action that is likely to happen in the future and continue for an expected length of time
- for an action that will be in progress at some point in the future
- for action verbs (e.g. running)
- for predictions about future events
Adverb used with Future Continuous:
- tomorrow (e.g. tomorrow at 5 o'clock)
Útil en búsqueda activa de complicaciones
Structure:
Will + Subject + Be +Verb-ING?
e.g. Will you be having fun at the party?
Mejor visualización cálculos biliares
Structure:
Subject + Won’t Be + Verb-ING
e.g. He won’t be having fun at the party.
Realza contraste en pared de vesícula biliar
Structure:
Subject + Will Be + Verb-ING
e.g. You will be having fun at the party.
Ecografía Abdominal
Future Simple is used:
- to predict an event in the future
- to invite
- to give orders
- to express willingness
- for actions that have not yet occurred but that will occur at a future date
Signo Murphy ecográfico positivo
Agrandamiento Vesícula >8 x 4 cm
Colgajo Intraluminal
Pared vesicular <4mm
Cálculos biliare sy detritos en vesícula biliar
'Going to' Future is used:
- to talk about our future intentions and plans
- for commands
Some adverbs used with 'Going to' Future:
- later
- tonight
- tomorrow
- next week
- next month
- next year
Líquido pericolecístico
Future Simple with 'will'' is used:
- to predict the future
- for something with absolute certainty
- when we're talking about a decision at the moment of speaking
- promises, requests, refusals, offers
- future facts
Some adverbs used with Future Simple:
- tomorrow
- next week
- next month
- next year
Criterios Severidad
There are four Past tenses:
- Past Simple
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect Simple
- Past Perfect Continuous
Grado I (leve)
Past Perfect Simple is used for:
- an action that began in the past and is still going on at the moment of speaking
- an action that continued before and after another action
- a change of mind
- an action happening repeatedly in the past
The Past Perfect tense is not normally used alone. It is used to denote the earlier of two past actions. We use Past Simple for the latter action.
Some adverbs used with Past Perfect Simple:
- already, before, ever, never
- once, twice, yet
- just, up to then
- for, since
No cumple criterios de Grado II o III
Structure:
Subject + had + Past Participle
e.g. They had already met Julia before the party.
Grado II (moderado)
Past Continuous is used for:
- an action that happened before another action in the past
- an action that started in the past and continued up to a given time in the past
- an action done several times up to a point in the past and continued to do after that point
- an action that happened in the past but is important at the time of reporting
Some adverbs used with Past Continuous:
- always, only, never, ever, still, just
4. Inflamación local marcada
Absceso hepático
Colecistitis Enfisematosa
Peritonitis biliar
Absceso piocolecistico
Colecistitis gangrenosa
3. Síntomas >72 horas
Structure:
Was/ were + Verb-ING?
e.g. Were you studying when she called?
2. Masa palpable en Hipocondrio Derecho
Structure:
Subject + wasn’t (was not)/ weren’t (were not) + Verb-ING
e.g. You were not studying when she called.
1. Leucocitosis >18.000
Structure:
Subject + was/ were + Verb-ING
e.g. You were studying when she called.
Grado III (severo)
Past simple expresses:
- an action that happened in the past and has no connection with the present
- an action that happened once in the past
- an action that happened regularly in the past
- an action that was true for some time in the past
- an event or action that already occurred
- an action that is finite - has both a starting and a stopping point
Some adverbs used with Past Simple:
- yesterday
- last month, last year
- ago (e.g. two days ago)
- in (e.g. in 1997)
- never, always, seldom, often, frequently, occasionally, once, twice
6. Disfunción Hematológica
Plaquetas < 100.000
5. Disfunción Hepática
PT - INR >1.5
4. Disfunción Renal
Creatinina >2
Oliguria
3. Disfunción Respiratoria
Structure:
Did + subject + Base Form of the Verb?
e.g. Where did you meet her?
PaO2/FiO2 <300
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
Was I?Were you?Was he/she/it?Were we?Were you?Were they?
Form of word "to have":
Did I have?Did you have?Did he/she/it have?Did we have?Did you have?Did they have?
2. Disfunción Neurológica
Structure:
Subject + did not/didn’t + Base Form of the Verb
e.g. They didn’t like my food.
Alteración conciencia
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
I was notYou were notHe/She/It was notWe were notYou were notThey were not
Form of word "to have":
I did not haveYou did not haveHe/She/It did not haveWe did not haveYou did not haveThey did not have
1. Disfunción Cardiovascular
Structure:
Subject + Verb in Past Simple (2nd form)
e.g. They lived in Spain three years ago.
Hipotensión con requerimiento vasoactivo
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I wasYou wereHe/She/It wasWe wereYou wereThey were
Form of verb 'to have':
I hadYou hadHe/She/It hadWe hadYou hadThey had
Criterios Dx
There are four Present tenses:
- Present Simple
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
C. Hallazgos Imagenológicos
Present Perfect is used for:
- an action that occurred at a time which is indefinite and has its effect on the subject
- an action that occurred many times and has the possibility to occur in the present/future
- an action that began in the past and is still going on in the present
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect:
- just
- already
- yet
- for
- never/ever
- up to now
Líquido perivesicular
Structure:
Have/ has +Subject+ Past Participle?
e.g. Has she finished the letter?
Vesícula > 8 x 4 cm
Structure:
Subject + haven’t (have not)/ hasn’t (has not) + Past Participle
e.g. She hasn’t finished the letter.
Engrosamiento pared vesicular >4mm
Structure:
Subject + have/ has + Past Participle (3rd Form of the Verb)
e.g. She has finished the letter.
B. Signos Sistémicos de Inflamación
Present Continuous is used to indicate the ongoing time (now).
Some adverbs used with Present Continuous:
- now, right now
- at this moment
- at the moment
- continually
- perpetually
- this year
- this season
- forever
PCR positiva
Structure:
BE + Subject + Verb-ING?
Are you eating now?
Leucocitosis
Structure:
Subject + BE not + Verb-ING
e.g. You are not eating now.
Fiebre
Structure:
Subject + BE (am/is/are) + Verb-ING
e.g. You are eating now.
A. Signos Locales de Inflamación
Present Simple is used for:
- habits
- general truths
- repeated actions of events
- fixed arrangements/timetables
- feelings/opinions/beliefs
- instructions.
Some adverbs used with Present Simple:
- always
- usually
- seldom
- never
- sometimes
- often
- frequently, generally
- habitually, occasionally
- once, twice
Masa, Dolor o Molestias en Hipocondrio Derecho
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + do not / don’t + V1 (First Form of Verb)
Subject (He, She, It) + does not / doesn’t + V1 (First Form of Verb)
e.g. He doesn’t work in a bank.
Signo Murphy positivo
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I usually go jogging at weekends.
Subject (He, She, It)+ V1(First Form of Verb) + s/es
e.g. She writes every day.