Part of a Computerd
Operating systems
Storage Management:usually refers to the
management of Computer data storage,
which includes memory management. It
can also refer to specific methods or
products for storage management, such
as the following.
Device Management:Within the computer,
activating and controlling the peripheral
devices. In a desktop computer, the
operating system interacts with the device
drivers for peripheral control.
User Interface: in the industrial
design field of human–computer
interaction, is the space
where interactions between
humans and machines occur.
Memory Management:is the process of
controlling and coordinating computer
memory, assigning portions called blocks
to various running programs to
optimize overall system performance.
Process Management: refers to aligning
processes with an organization's strategic
goals, designing and implementing process
architectures, establishing process
measurement systems that align with
organizational goals, and educating and
organizing managers so that
they will manage processes effectively.
PORTS, PEREPHERIALS, EXPANSIONs
make it a different color
otherthan the under captions
Printer: is a device that
accepts text and graphic
output from a computer
and transfers the
information to paper,
usually to standard size
sheets of paper. Printers
vary in size, speed,
sophistication, and cost.
In general, more expensive
printers are used for
higher-resolution color printing.
MicroPhone/Mic: is a device that
captures audio by converting sound
waves into an electrical signal. This
signal can be amplified as an
analog signal or may be converted
to a digital signal, which can be
processed by a computer or other
digital audio device.
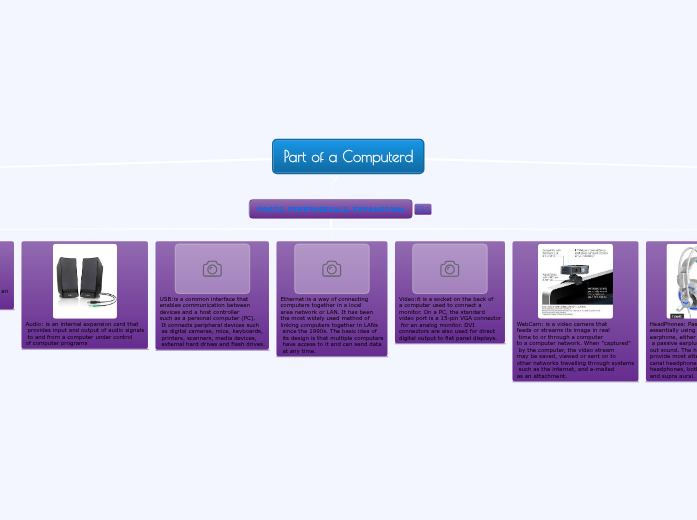
HeadPhones: Passive noise isolation is
essentially using the body of the
earphone, either over or in the ear, as
a passive earplug that simply blocks
out sound. The headphone types that
provide most attenuation are in-ear
canal headphones and closed-back
headphones, both circumaural
and supra aural.
WebCam: is a video camera that
feeds or streams its image in real
time to or through a computer
to a computer network. When "captured"
by the computer, the video stream
may be saved, viewed or sent on to
other networks travelling through systems
such as the internet, and e-mailed
as an attachment.
Video:it is a socket on the back of
a computer used to connect a
monitor. On a PC, the standard
video port is a 15-pin VGA connector
for an analog monitor. DVI
connectors are also used for direct
digital output to flat panel displays.
Ethernet:is a way of connecting
computers together in a local
area network or LAN. It has been
the most widely used method of
linking computers together in LANs
since the 1990s. The basic idea of
its design is that multiple computers
have access to it and can send data
at any time.
USB:is a common interface that
enables communication between
devices and a host controller
such as a personal computer (PC).
It connects peripheral devices such
as digital cameras, mice, keyboards,
printers, scanners, media devices,
external hard drives and flash drives.
Audio: is an internal expansion card that
provides input and output of audio signals
to and from a computer under control
of computer programs
Monitor: A computer monitor is an
output device which displays
information in pictorial form.
Graphics Card: a microprocessor
specialized for video calculations
Keyboard: The phrase cooling in computing
generally refers to the dissipation of large
amounts of heat, which is created while a
computer system is running.
CORE
Cooling Devices: in computing
generally refers to the dissipation
of large amounts of heat, which
is created while a computer system
is running. Heat is generated
inside the computer tower by
various hardware such as CPU, video
card or even the hard drive.
Drives: Removable disk is any drive or disk
that can be transported between computers.
Ram: Is the physical hardware
inside the computer that temporarily
stores data, serving as the computer's
"working memory".
CPU:The CPU sends signals to control
the other parts of the computer, almost
like how a brain controls a body.
MotherBoard: Main circuit board
of the computer that connects
everything