Water on Earth
Geography
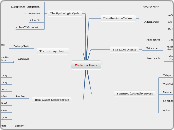
Water on Earth
How Rivers affect people
Negative
Flooding
Positive
Means of transport
Production of hydroelectric power
Source of drinking water and food
Recreation and tourism
Water supply for industry
Fertile soil for farming
Water supply for farming
Features formed by Rivers
Deltas
Formed where layers of sediment are deposited at the river mouth over time
Floodplains
A low-laying land that becomes flooded when a river overflows its banks
Meanders
A bend or curve in a river
Waterfalls
A vertical flow of fast-moving water falling from a great height
Valleys
A low area between hills or mountains
The Drainage Basin
Watershed
the area that is drained by a river and its tributaries is called the drainage basin
Drainage Basin
he boundary of a drainage basin is marked by the tops of the surrounding highland
The River system
River mouth
The end of the river wehn it flows into a lake or sea
Tributaries
the streams and rivers that join a main river
River source
The place at which a river begins
The Hydrologic Cycle
4. Runoff / Groundwater
3. Rainfall
2. Condensation
1. Evaporation / Transpiration
Also known as water cycle
Distribution of Water
3% fresh water
1% found in streams/lakes/rivers
29% found underground
70% is frozen
97% salt water

