by Timothy Nguyen 3 years ago
169
Module 3 Concept Map
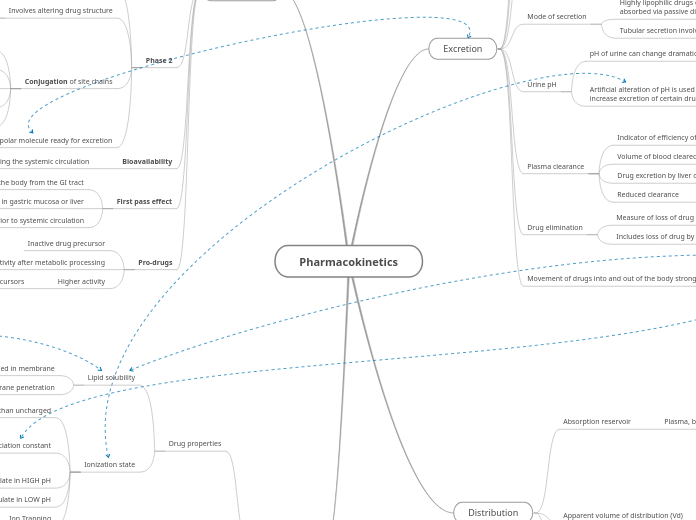
by Timothy Nguyen 3 years ago
169

More like this
E.g. Organic cation transporters
Mediate the movement of dopamine and choline
Facilitates transport single species IN THE DIRECTION of its electrochemical gradient
Facilitated diffusion is passive with no energy
ABC transporters
Mediate removal of drugs from cells
E.g. P‐glycoprotein transporters
Primary group of ABC transporters
Transport AGAINST concentration gradients
Specialized membrane proteins
Ion Trapping
Drug's ionization preference and retention
Basic drug will accumulate in LOW pH
Acidic drug will accumulate in HIGH pH
Dissociation constant
Negative value = greater proportion of non-ionized drug
Greater lipid solubility
Ratio between dissociated ions and drug
Ionized dissolve aqueous fluids than uncharged
High soluble = higher membrane penetration
Too lipid-soluble = retained in membrane
Different absorption or distribution properties than precursors
Glycine or water addition
Methylation
Glutathione addition
Sulphation
Glucuronidation
Normally results in inactive product (some exceptions)
Reduce intrinsic efficacy for excretion
Can also occur in other tissues like lungs and kidneys
P450 enzyme levels regulated by external factors
E.g. grapefruit juice and Brussels sprouts
Genetic variations exist
Primary cause of patient response variation
Net effect of cytochrome p450 cycle is addition of oxygen or hydroxyl
3 main CYP gene families
CYP3
CYP2
CYP1
Need to cross cell membrane to reach cytochrome systems
Can also occur in other tissues or plasma
Hepatic cytoplasmic microsomal enzymes
E.g. cytochrome systems
Diffusion is PRIMARY for drugs crossing BBB
Active transport by carriers
AA, glucose, amines and purines
Highly lipophilic drugs able to readily pass through
Molecule must pass through at least 2 membranes
Gaps that allow solute diffusion
Fat ~20%
Intracellular water ~35%
Interstitial water ~16%
Plasma water ~5%
Transcellular water ~2%
Comprises CSF, intraocular, peritoneal, pleural and synovial fluids and digestive secretions
Indicative of function impairment of excretory organ
Clearance is a constant for any given drug
Alkaline urine increases acidic drug excretion
Acidic urine increases basic drug excretion
Ion trapping to increase drug retention in urine
Due to diet or drug intake
Less free drug for filtration and diffusion
Plasma proteins too large to pass renal luminal barrier
Retained in circulation