作者:Rory Marleau 3 年以前
303
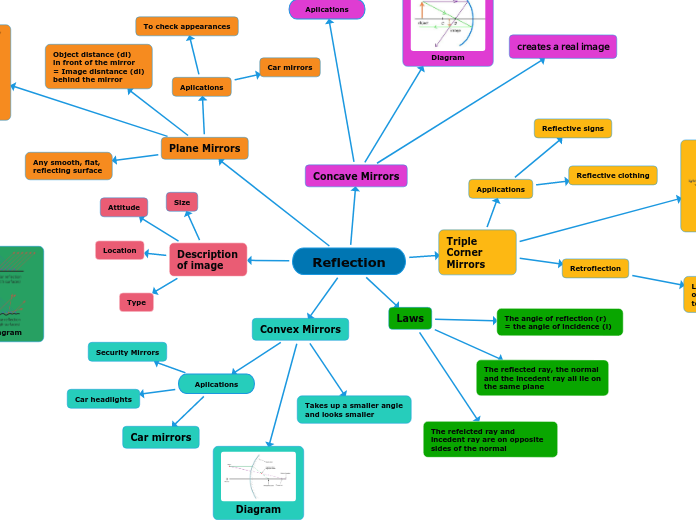
Reflection
Specular
Diffuse
Rough surfaces
The normals are all facing different directions
< r are all different from each other
Smooth and flat surfaces
All normals are perpendicular to the surface < i = < r
Reflection
Description of image
Type
Location
Attitude
Size
Laws
The reflected ray, the normal and the incedent ray all lie on the same plane
The refelcted ray and incedent ray are on opposite sides of the normal
The angle of reflection (r) = the angle of incidence (i)
Concave Mirrors
creates a real image
Magnifying glasses
Teloscopes
cosmetic or magnifying mirrors
Plane Mirrors
To check appearances
Object distance (di)
in front of the mirror
= Image disntance (di)
behind the mirror
Any smooth, flat, reflecting surface
Triple Corner Mirrors
Retroflection
Light rays bouncing off and shining back to the source
Applications
Reflective clothing
Reflective signs
Convex Mirrors
Diagram
Takes up a smaller angle and looks smaller
Aplications
Car mirrors
Security Mirrors
Car headlights

