por SADAT MOHAMMAD ABDULLAH 26 dias atrás
49
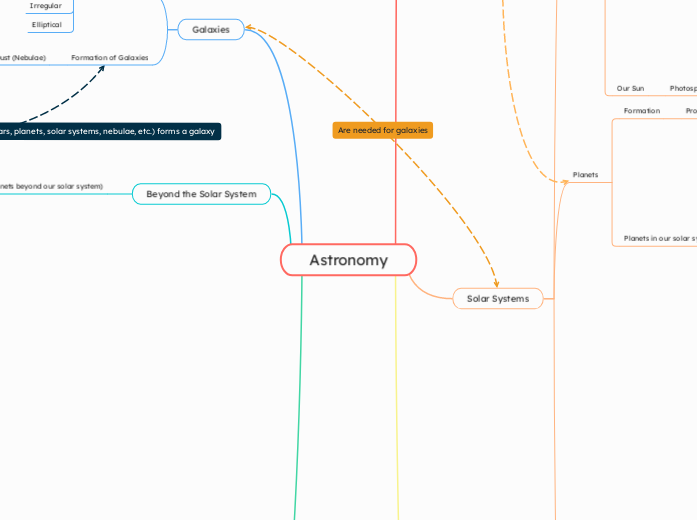
Astronomy
por SADAT MOHAMMAD ABDULLAH 26 dias atrás
49

General Theory of Relativity: Gravity distorts space and time.
Special Theory of Relativity: Time dilation, All movement is relative and speed of light has a limit, time slows down as we speed up
Circular: Speed doesn't create eccentricity (perfect conditions)
Hyperbolic: Great speed or distance
Spiral: Low mass or speed
2. Equal area in equal time (Planets move faster near the Sun)
1. All planetary motion is elliptical
Swirl of Dust (Protoplanetary Disk)
Star
Used for interstellar distances
Used for distances within our Solar System
Trans-Neptunian Objects (Objects beyond the orbit of Neptune
Kuiper Belt (Disk shaped group of millions of small objects orbiting the Sun and are thought to be from the formation of the Solar System
Oort Cloud (Spherical, Icy cloud of small debris)
The Asteroid Belt is a band of asteroids that orbit the sun in between Mars and Jupiter
Asteroids are thought to be debris left over from the formation of the Solar System, non-spherical, small, some have moons
Meteoroids (Pieces of rocks moving through space, thought to be broken parts of asteroids and planets)
Meteors (Meteoroids that enter the Earth's atmosphere and begin to burn up due to atmospheric friction)
Meteorites are the surviving meteors (ones that reached the ground without fully burning up)
Meteor Showers are what people also call "Shooting Stars", though they aren't stars and are in fact meteors, when the Earth passes through an area filled with these meteors, a meteor shower occurs
Tides
Tides occur due to the gravitational difference of the Moon and the Earth
Eclipses
Lunar Eclipse
Can only occur during a full moon, the Earth passes in between the Sun and the moon and can result in a partial lunar eclipse (penumbra shadow) or a total lunar eclipse (umbra shadow), the moon's orbit is tilting resulting in only 2 lunar eclipses on average per year, the moon can appear reddish during a lunar eclipse and is completely safe to watch
Solar Eclipse
Can only occur during a new moon, the Moon's shadow falls on the Earth's surface and is in between the Sun and the Earth, on average only twice a year however, due to the shadow's size being smaller, you often have to be in a remote or specific place to see the solar eclipse, it is not safe to look at the solar eclipse with just your eyes as the radiation can damage them
Penumbra and umbra are the inner and outer shadow of the Earth
When a celestial object moves directly in front of another celestial object
Phases of the moon
Waning Crescent
Third Quarter
Waning Gibbous
Full Moon
Waxing Gibbous
First Quarter
Waxing Crescent
New Moon
Moon phases are created by the reflection of sunlight on its surface (always half-luminated, what we see is based on where the moon is relative to Earth
Satelites (Celestial object orbiting another celestial object)
Jovian (Gaseous)
Neptune
Furthest planet from sun, similar to Uranus
Uranus
Rotates on its side, rings, methane gas atmosphere
Saturn
Main composition of atmosphere: H & He, Rings
Jupiter
Gas Giant, Largest planet, Massive Red Storm
Terrestrial
Mars
Red Planet due to high concentration of Fe in its rocks, 2 polar ice caps, thin atmosphere
Earth
Only discovery of life, water in 3 forms, perfect atmosphere, temperature, etc.
Venus
Acid Rain (Sulfuric Acid), Dense atmosphere trapping heat, Hottest planet, Earth's sister, Similar to earth in size and composition
Mercury
No atmosphere, From Extremely hot to freezing cold, smallest planet
Protostar (Gravitational Center)
Swirling dust and Hydrogen gas
Planetesimals
Photosphere (Surface layer of the Sun)
Sunspots (Charged Particles disturb the photosphere and appear darker due to the difference in temperature and create strong magnetic fields)
Solar Flares (Ejections of intense steam of charged particles into space, these steams are known as "Solar Wind", upon the interaction of solar winds and our Earth we get auroras which are just the charged particles passing through our magnetic fields, generating electric current that flows to our poles and charges gases, creating light
Stars radiate the entire electromagnetic (EM) spectrum which tells us about them
Radio
Microwave
Infrared
Visible
Ultraviolets
X-rays
Gamma rays
>8Ms
Blue Giant
Red Supergiant
Supernova (No more nuclear fusion, Gravity collapses core, chemical composition: To U)
(If >20Ms)
Black Hole (Gravity pulls in on itself, so dense that light can't even escape its gravitational pull)
Neutron Star (Dense, small, rotates incredibly fast)
>10Ms
(1x10^9 years of lifetime, Short life)
Chemical Composition: To Fe
1-8Ms
Yellow Star
Chemical Composition: To C
Red Giant
Planetary Nebula (Outer layers of star expel into space)
Core compresses
Black Dwarf
(1x10^10 years of lifetime, Average life)
<1Ms
Red Dwarf
(1x10^12 years of lifetime, Long life )
H -> He
Heats up due to nuclear fusion (becomes white dwarf)
Black Dwarf (Cools Down)
Ms = Solar Mass (Relative to Sun's Mass)
Supergiants
Cooler, extremely large, extremely bright
Giants
Cool, large, bright
Main Sequence
90% of all stars
White Dwarf
Dense, hot, small
Hydrogen Gas + Dust (Nebulae)
Protostar
At 1x10^7°C, Nuclear Fusion occurs
Forces Balance (Gravity Inward, Fusion Outward)
Balance = Stable Star
H -> He (It goes on Depending on the mass of the star)
Nuclear Fusion = Fusion of 2 or more atomic Nuclei