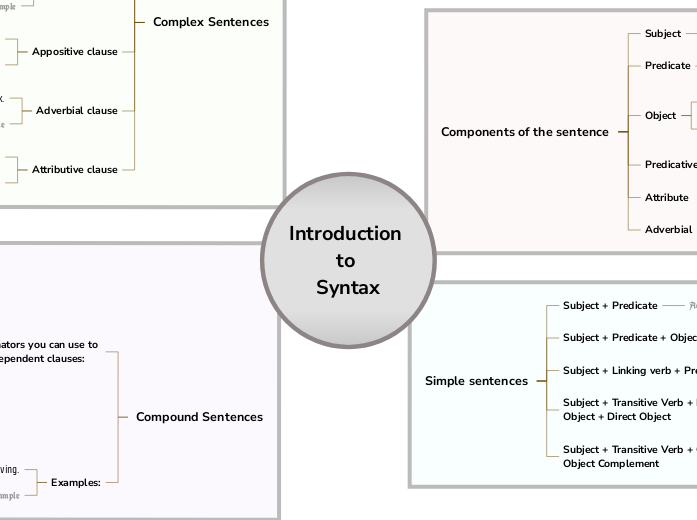
Use this template to learn about the syntax and understand phrase components and subordinate clauses. The components of the sentence are subject, predicate, object, predicative, attribute, and adverbial. These are used to form different types of sentences: simple sentences, compound sentences, and complex sentences. In linguistics, syntax is the set of rules, principles, and processes that govern the structure of sentences in a given language, usually including word order. A compound sentence is a sentence that has at least two independent clauses joined by a comma, semicolon or conjunction. An independent clause is a clause that has a subject and verb and forms a complete thought. Create your own compound sentences, using the coordinators above. When independent clauses are joined with coordinators (also called coordinating conjunctions), commas and semicolons, they do more than just join the clauses. They add meaning and flow to your writing. A complex sentence is a sentence that contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses. Attributive clauses serve as an attribute to a noun (pronoun) in the main clause. This noun or pronoun is called the antecedent of the clause. An adverbial clause is a group of two or more words that function as an adverb in a sentence. An appositive clause follows another noun or noun phrase in apposition to it; that is, it provides information that further identifies or defines it. The subject clause is a dependent clause that acts as a subject. A predicative clause may be introduced by conjunctions - that, whether, whether... or, as, as if, as though, because, lest, the way - or connectives. The object clause is a phrase on which a verb performs an action. It falls at the end of a sentence, and is governed by a verb or a preposition. See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences. See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences. See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences. See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences. See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences. An adverbial is an individual word (that is, an adverb), a phrase, or a clause that can modify a verb, an adjective, or a complete sentence. The attribute is defined as a quality or characteristic of a person, place or thing. The predicative is defined as an adjective or noun forming or contained in the predicate. Traditional grammar defines the object in a sentence as the entity that is acted upon by the subject. The indirect object identifies the person/thing for whom/which the action of the verb is performed. The direct object is the receiver of the action mentioned in the sentence. The predicate of a sentence is the part that modifies the subject in some way. Because the subject is the person, place, or thing that a sentence is about, the predicate must contain a verb explaining what the subject does and can also include a modifier. The subject of a sentence is the person, place, thing, or idea that is doing or being something. You can find the subject of a sentence if you can find the verb. A gondolattérképek segítenek az ötletelésben, a fogalmak közötti kapcsolatok kialakításában, a rendszerezésben és az ötletek generálásában. A gondolattérkép-sablonok azonban könnyebb utat kínálnak a kezdéshez, mivel ezek olyan keretek, amelyek egy adott témával kapcsolatos információkat tartalmaznak, irányadó utasításokkal. Lényegében a gondolattérkép minták biztosítják azt a struktúrát, amely egy adott téma összes elemét egyesíti, és kiindulópontként szolgál az Ön személyes gondolattérképjéhez. Forrást jelentenek arra, hogy praktikus megoldást nyújtsanak egy adott témával kapcsolatos gondolattérkép létrehozásához, akár üzleti, akár oktatási céllal. A Mindomo intelligens gondolattérkép-sablonokat kínál, amelyek lehetővé teszik, hogy könnyedén működjön és gondolkodjon. Választhat a Mindomo üzleti vagy oktatási fiókjaiból, vagy létrehozhatja saját gondolattérkép sablonjait a semmiből. Bármilyen gondolattérkép átalakítható gondolattérkép-sablon térképpé, ha az egyik témakörhöz további irányadó jegyzeteket ad hozzá.Introduction to Syntax
Introduction to Syntax
Compound Sentences
Examples:
Tim is tired, yet he's driving.
Coordinators you can use to join independent clauses:
Other
So
Yet
Or
But
Nor
And
For
Complex Sentences
An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence, but a dependent clause even though it has a subject and a verb cannot stand alone.Attributive clause
He went to the next house, which stood in a small garden.
Adverbial clause
We couldn't park anywhere near the park.
Appositive clause
Chopin, a Polish composer, was one of the most celebrated pianists of his day.
Subject clause
We like the person who teaches us German.
Predicative clause
The latter may be conjunctive pronouns - who, whoever, what, whatever, which - or conjunctive adverbs - where, wherever, when, whenever, how, why.The question is whether we can manage without him.
Object Clause
We didn’t realize she was so ill.
Simple sentences
Subject + Transitive Verb + Object + Object Complement
Tim is driving the red car.Subject + Transitive Verb + Indirect Object + Direct Object
Tim is driving the car with his mother.Subject + Linking verb + Predicative
Tim is the driver.Subject + Predicate + Object
Tim drives the car. Subject + Predicate
Tim drives.Components of the sentence
Adverbial
Attribute
Predicative
Its main trait is that it serves to express a property that is assigned to a 'subject'.
For e.g.: The dog is old.Object
Indirect object
The indirect object is usually a person or a thing.Direct object
Predicate
Subject
Ask the question, 'Who or what 'verbs' or 'verbed'?' and the answer to that question is the subject.Add example
Miért érdemes Mindomo gondolattérkép mintát használni?
Egy sablon különböző funkciókkal rendelkezik: