Effectively manage and organize your business projects using the Advanced Business Project template. This template provides a structured framework to gather and maintain all essential information for small to medium-sized projects. The map is designed with a clear sequence, including a start, iterative phases, and an end, making it adaptable to both waterfall and Agile project management approaches. Begin by outlining your project goals, tasks, and milestones, then use the template to track progress and adjust as needed. This advanced template assumes familiarity with basic Mindomo features and helps ensure comprehensive project planning and execution. An Inbox topic is useful for any kind of map. Use it to quickly capture new ideas and information before integrating them into the map. This template contains tips and guidance in the Template pop-up dialogue. Instead of following it one step at a time, feel free to click around in the map to read the guidance notes. You can work on the map in any order, although it makes sense to do most stages 1 and before starting delivery. No project lasts forever. Some projects get canceled, some are completed under duress, and some are successful. In all cases, you can learn from the results. Write here additional info related to the closing stage. What learning from your project can be transferred to others in your knowledge management system? Type in an idea for your knowledge management system. What process and checklist changes are needed to pre-empt issues that your project encountered? Type in what you should have changed. Review the latest iteration of the project and make changes. Prepare required reporting for other stakeholders, e.g. a monthly financial status report. What is the information that you would like to report to stakeholders? Update the project log with important decisions that affect the project. What is an important decision that affect the project? Make necessary changes to the delivery plan in response to issues or changes that have taken place. What changes are necessary for the delivery plan? Review whether technical debt (necessary redesign or refactoring) is building up in your project and what impact this is having. What should you redesign or refactor? Take steps to ensure that capacity will meet budget and time constraints. Type in a step to ensure that capacity will meet budget and time constraints. Take steps to provide necessary capabilities, e.g. training additional resources. Type in a step to provide necessary capabilities. Make changes to the project processes in response to issues that have arisen. What change would you like to make to the project processes? Manage the current iteration (delivery phase or sprint). This activity takes place in parallel to the delivery activities. Ensure that deliverables are formally accepted by the client at the end of this stage or iteration. Maintain and update the design, if necessary to resolve issues and accommodate changes. Type in a design update. Maintain and update the specifications. It is usual for specifications to need clarification at the point at which they are implemented, even though they might have seemed perfectly clear beforehand. It is also common for the client to update and refine specifications. Type in a specification update. Review and update the risk register. Consider whether: Type in a risk register update. Resolve issues that arise during this delivery iteration that block the project. Type in an issue that you have encountered. Priority Establish the priority to solve this issue: Deliver the next iteration of the project. Some of the work in an iteration might be 'refactoring', or tidying up previous work as a foundation for future work. You cannot save time by omitting this or allowing technical debt to build up. Leaving it late in the project simply makes the task more complex, or risks the project becoming unmaintainable. Type in a refactoring idea. Users, customers, or other authorized entities do this test to determine application/software needs and business processes. Find some business processes. Business process Type in a business process. Find some application needs. Aplication need Type in an application need. Prepare deliverables for this iteration, based on the plan and specification. Type in a deliverable. Start delivery and management activities in parallel. Gather and organize the basic information that you will need for your project. Maintain a log of important decisions made in the project. This can inform changes to your project processes, if you find yourself making decisions that could have been taken earlier with less impact. Type in an important decision made in the project. Plan the project budget and controls. Budget What is the budget for your project? The plan for producing the project deliverables on schedule. Project type What type of project do you plan? Plan the communications with stakeholders to ensure that people are kept up to date and informed. Your plan will probably include methods (such as dashboards or intranet sites) and events such as regular meetings. Prepare a risk catalog for your project. List the risks that are outside your risk appetite, and what you are doing to reduce their likelihood or impact. Within your risk appetite Add a risk that is within your risk appetite. Outside your risk appetite Add a risk that is outside your risk appetite. Risk Define your 'risk appetite' for your project. Define your risk appetite. Prepare a list of processes or checklists that you will need to run the project. Checklists are useful for routine procedures. If you don't use checklists, consider creating some to ensure consistency and save time. Examples include: Checklist Type in the checklist name. Task Type in a task from the checklist. Add links to or define the processes that you will need to execute your project. Examples include: Process Add link to the process These are the resources that you will need to complete your project. What research and information is necessary for your project? Tools and equipment that will be needed for your project. Tool Type in a tool that will be needed for your project. The knowledge and skills that will be needed to complete your project. Knowledge or skill Type in a skill or knowledge that will be needed to complete the template. Expert Who is your expert? Team member Type in your team member's name and role. Prepare a design that will implement the deliverables and essential requirements. Type in an idea for the design. Collect the requirements for the project. Prepare a list of deliverables that the client will receive. For clarity, you may prefer to explicitly state exclusions from the requirements and deliverables. Non-functional requirements typically include: Type in the name of the requirement. Requirements describing specific artifacts, features, and functions that the project delivers. Requirement Type in the name of a requirement. Create a project dictionary to define technical terms and jargon used in your project. Don't assume that the same terms mean the same things to everyone. Type in the term. Users The project dictionary should include descriptions of the users and their primary roles in relation to the project outcome. User Type in the name of a user. The basic project flow consists of 6 steps: Identify all the project stakeholders, including: Type in the name and the role of the shakeholder. Ensure that project contracts and purchase orders are in place and are properly reviewed and accepted. Add links to those documents for reference. Add link to the document for reference What is the vision and strategy for the project? These will engage stakeholders and the project team, not the project plan. It will be important to communicate both the vision and the strategy to the team. Type in the project vision. Le mappe mentali aiutano a fare brainstorming, a stabilire relazioni tra i concetti, a organizzare e generare idee. Tuttavia, i modelli di mappe concettuali e mentali vuote offrono un modo più semplice per iniziare, in quanto sono strutture che contengono informazioni su un argomento specifico con istruzioni guida. In sostanza, i modelli di mappe mentali garantiscono la struttura che combina tutti gli elementi di un argomento specifico e servono come punto di partenza per la vostra mappa mentale personale. Sono una risorsa che fornisce una soluzione pratica per creare una mappa mentale su un particolare argomento, sia per il lavoro che per l'istruzione. Mindomo offre modelli di mappe mentali intelligenti che consentono di lavorare e pensare senza sforzo. È possibile scegliere tra una varietà di modelli di mappe concettuali dagli account aziendali o educativi di Mindomo, oppure creare i propri modelli di mappe mentali da zero. Qualsiasi mappa mentale può essere trasformata in un modello di mappa concettuale aggiungendo ulteriori note guida a uno dei suoi argomenti.Advanced Business Project Template
This advanced business project template helps you gather, organize and maintain all the information needed for a small to medium-sized business project.
The map structure is a simple project sequence with a beginning, some iteration, and an end. This model can be applied to both waterfall and Agile projects.
This is an advanced template requiring familiarity with basic Mindomo features.
Keywords: Project management, business project, task management, business process, business organization, organizing information
Advanced business project template
Inbox
Periodically review the contents of the Inbox and empty it out by either moving topics to the right place in the main map, or discarding them.Advanced business project map
This project map is designed to help you capture all the information you will need to manage a small to medium sized project. If kept up to date, it will provide a project 'dashboard' through the lifecycle of the project, and will form an invaluable record that will help you with future projects.6. Close
'Project post-mortems' are a popular activity but on their own lead to very little learning. Nobody reads through previous project post-mortem reports before their next project. You must feed lessons into changes to process or updates to a knowledge base that is accessible outside the context of your project.Additional info
Knowledge gained
Process learning
Looking at your project log, how could unwelcome decisions have been reduced or avoided?5. Review
Reporting
Important decision
Update plan
Delivery change
Technical debt
Some technical debt can be tolerated, but if it begins to hamper future work it should be raised as an issue and resolved.Necessary redesign
Capacities
Capabilities
Step
Change
4. Manage
Acceptance of deliverables
Your project contract may permit staged invoicing on acceptance of milestones.Acceptance status
Design update
Specification update
Risk update
Issues
Maintain the issues log, keeping track of issues that will need to be resolved in the next project iteration.
Look for signs of upcoming issues so that they can be addressed before they become critical.Issue
3. Deliver
If this is a waterfall project, the delivery may be split up into stages.
If this is an Agile project, the delivery will be split up into sprints, each one refining the requirements.Refactoring
Refactoring idea
Acceptance tests
Business processes
Application needs
Raise issues that arise during the work.Deliverable
+
2. Prepare
Feel free to delete topics that are not relevant.Project log
Decision
Plans
Financial plan
Delivery plan
If your project is a waterfall project, you will need to plan through to the end of the project.
If your project is an Agile project, you will need to plan the next sprint in detail, while more distant sprints can have some flexibility depending on the outcomes from previous sprints.Communications plan
Different stakeholders will require different levels and frequency of information. You can use a RACI grid if you have a complex set of stakeholders.Risks
Risk catalogue
For completeness, you can also record the risks that are within risk appetite, but no remedial action is required unless your processes fail to deal with them.Risk appetite
Process catalogue
Checklists
Processes
Resources
Information
Tools and equipment
Knowledge and skills
People
Design
Idea
Requirements
Requirements may be expressed as User Stories for the users.
Requirements should be labeled asDeliverables
These deliverables will probably form the basis of project phases or sprints, and may also relate to stage payments.
Acceptance of deliverables by the client will be project milestones.Exclusions
Non-functional
Functional
These requirements should be measurable and testable.Dictionary
This dictionary underpins the requirements and reduces ambiguity.Term
1. Start
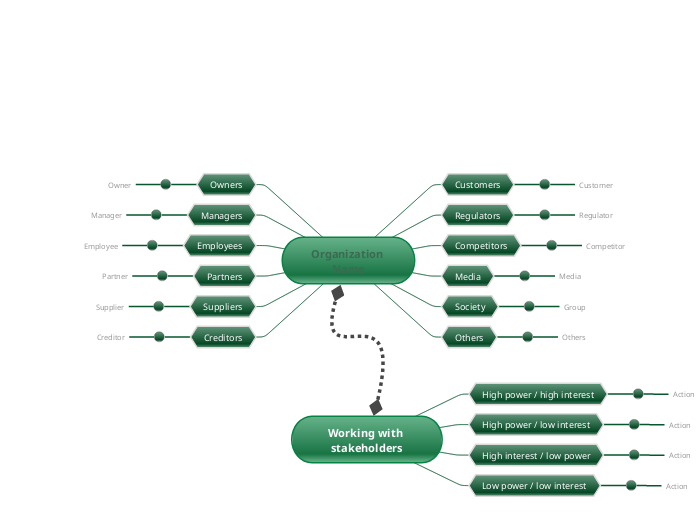
Stakeholders
Understanding the dynamics and relationships between the stakeholders is the key to anticipating major risks that may lie ahead in your project. Stakeholders with conflicting interests must be kept engaged.Stakeholder
Legal
Document
Project vision
A plan is what you will do while you are in control. A strategy is your decision-making framework when you are no longer in control, and external factors or random events take over.
Projects always start under control but many of them quickly succumb to 'unexpected' events. You need a vision, a strategy that will deliver the vision, and a working plan.Vision
Perché utilizzare un modello di mappa concettuale Mindomo?
Un modello ha diverse funzionalità: